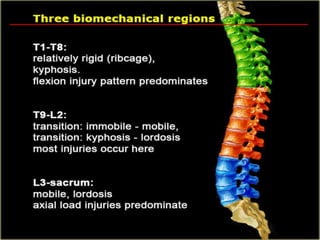
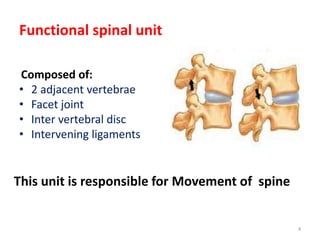
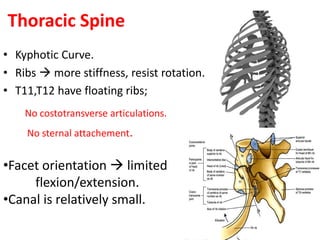
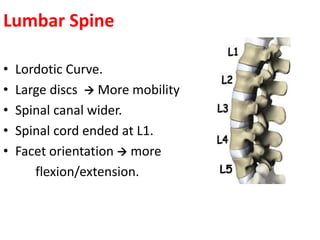
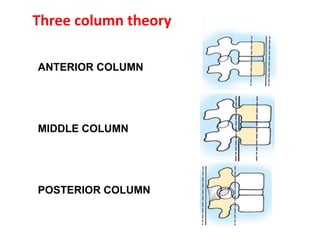
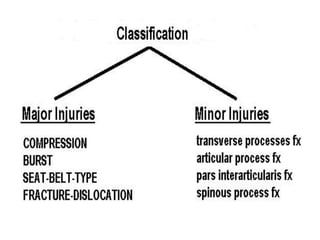
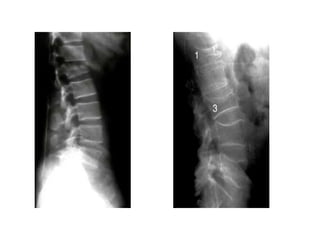
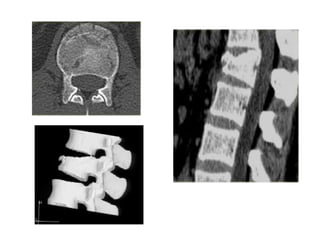
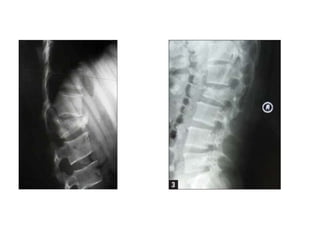
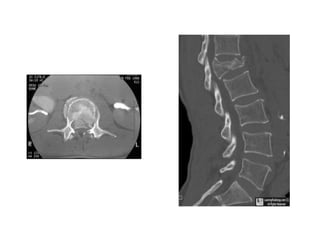
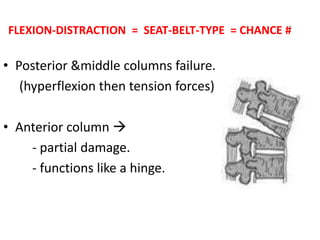
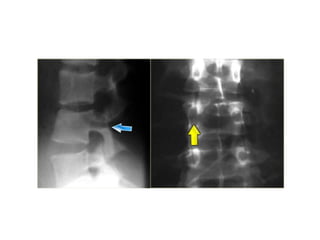
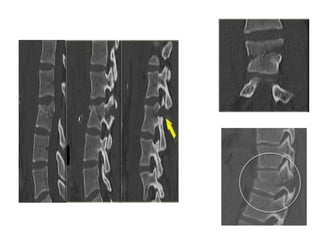
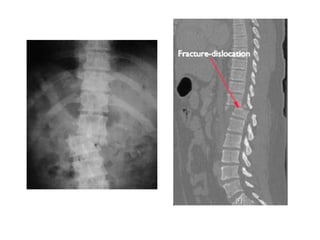
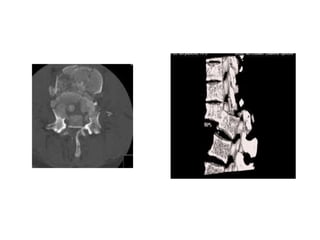
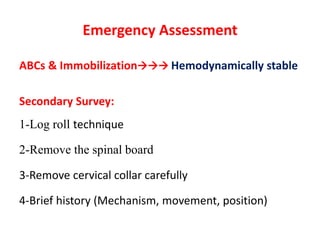
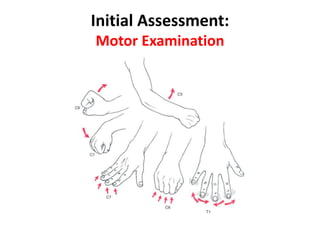
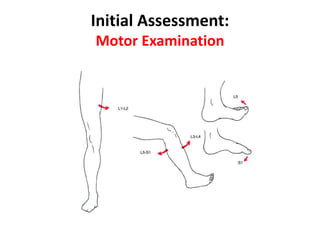
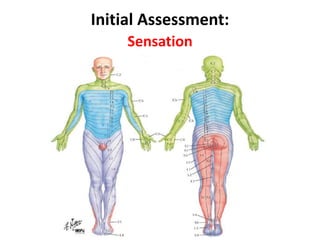
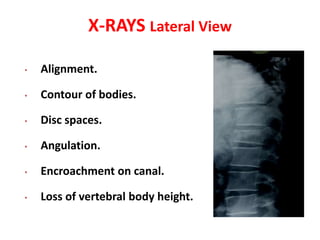
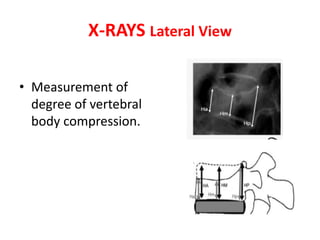
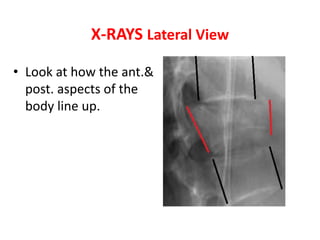
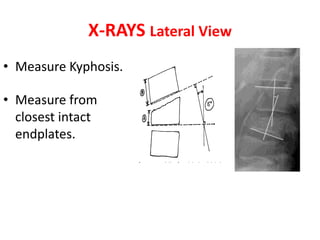
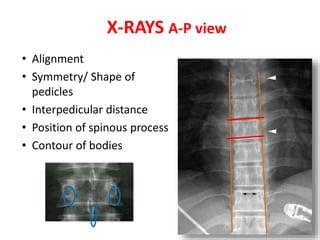
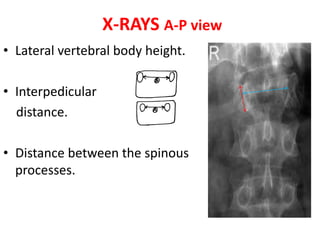
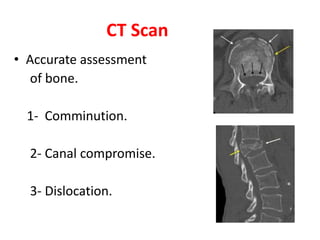
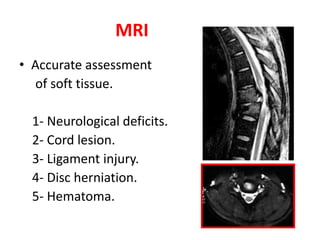
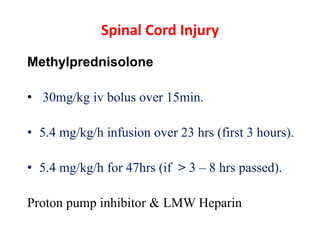
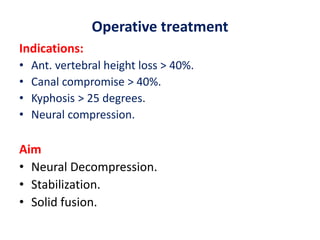
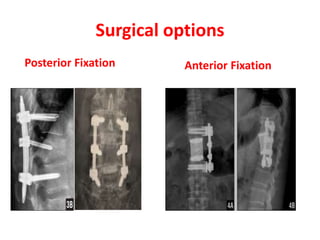
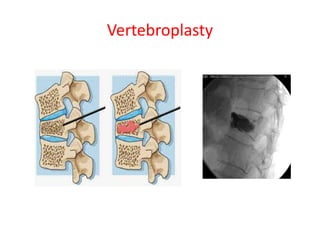
Thoracolumbar fractures account for 50% of spinal fractures and often occur between the T9 and L2 vertebrae. They are commonly caused by high-energy trauma like motor vehicle accidents or falls. Assessment involves neurological examination, imaging like x-rays and CT scans to evaluate bone injury and MRI to assess soft tissues. Treatment depends on factors like degree of vertebral compression and kyphosis, with non-operative options for mild cases and surgical stabilization and fusion for more severe injuries or neurological compromise. Rehabilitation focuses on restoring function, preventing complications, and bracing to solidify healing.