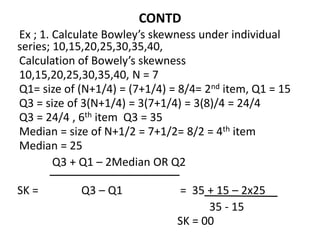
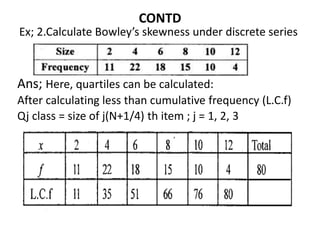
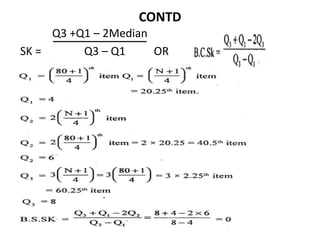
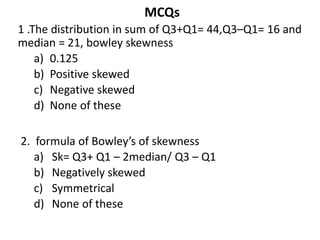
This document discusses Bowley's coefficient of skewness, which is a measure of the skewness of a data distribution based on the positions of the quartiles. It provides examples of calculating Bowley's skewness for individual and discrete data series by finding the first quartile, third quartile, and median. The document also includes multiple choice questions to test understanding of measures of skewness, Karl Pearson's coefficient of skewness, and Bowley's coefficient of skewness.