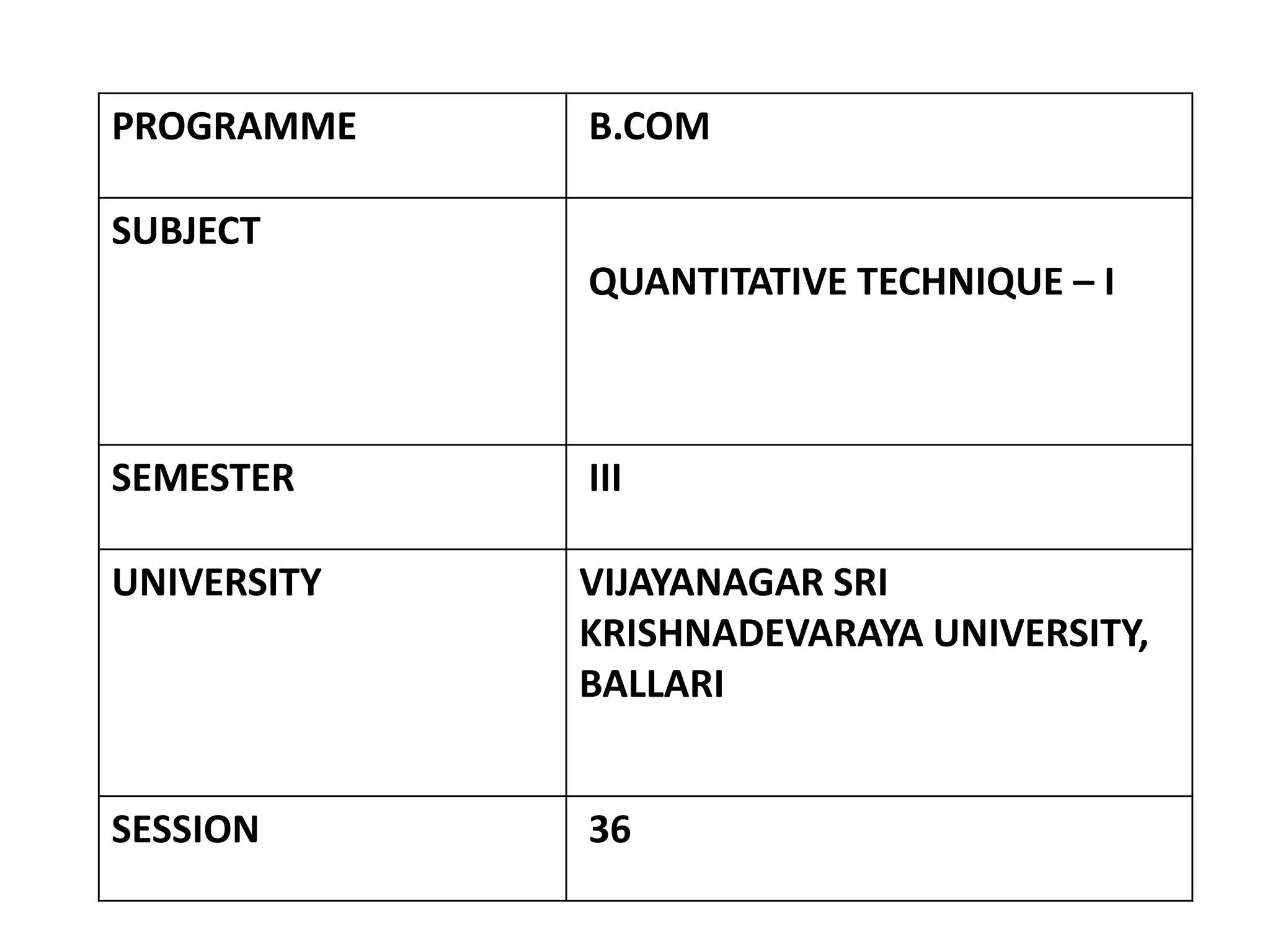
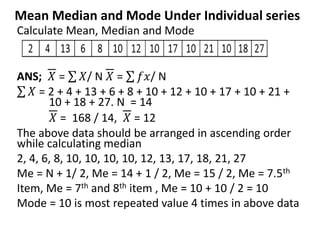
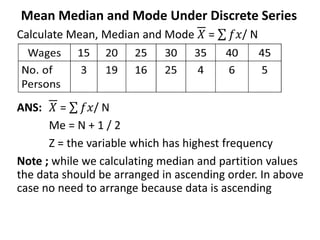
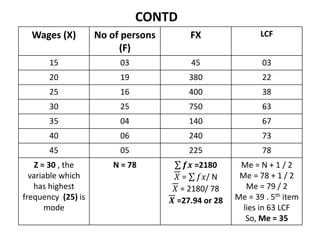
This document discusses a quantitative techniques course for a B.Com program. It covers measures of central tendency and dispersion, including the mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. The learning objectives are to understand these concepts and apply them to sample data. The session discusses calculating the mean, median, and mode for individual and discrete data series. It provides an example of calculating these values for a set of wage and employee data. Multiple choice questions review key aspects of the measures discussed.