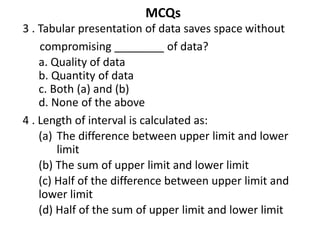
This document summarizes a session on tabulation of data from a quantitative techniques course. It defines tabulation as systematically organizing data in rows and columns in a table. The objectives of tabulation are to simplify complex data, highlight essential features, facilitate comparison and statistical analysis, and save space. Rules for effective tabulation include using an appropriate table size, arranging column and row headers systematically, clearly defining units of measurement, rounding figures, avoiding unnecessary details, making the table self-explanatory, and avoiding abbreviations. Multiple choice questions are provided to test understanding.