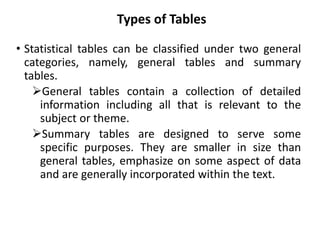
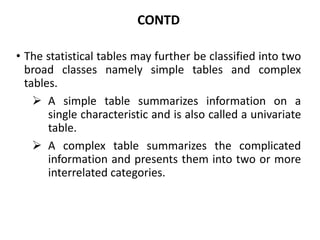
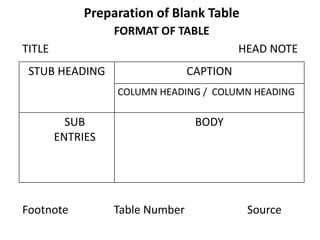
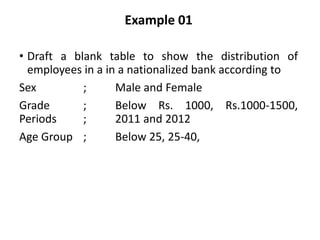
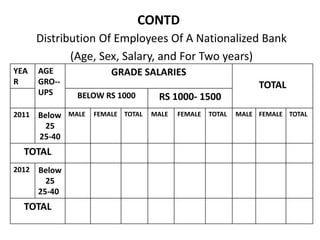
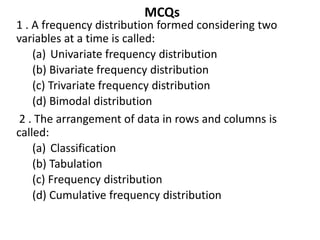
This document provides an overview of a quantitative techniques course for a B.Com program. It discusses the objectives of learning about tabulation, including presenting data in textual and tabular formats and constructing frequency distributions. It also covers types of tables like general tables and summary tables, as well as simple and complex tables. An example is provided for constructing a blank table to show employee distribution by sex, grade, age group, and year for a nationalized bank. Finally, it concludes with some multiple choice questions about topics like bivariate frequency distributions and the components of a statistical table.