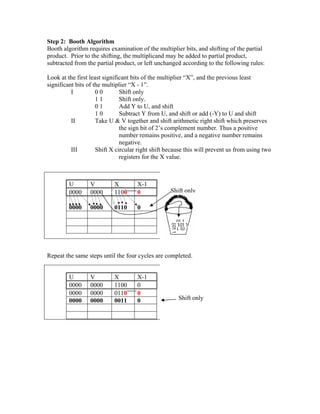
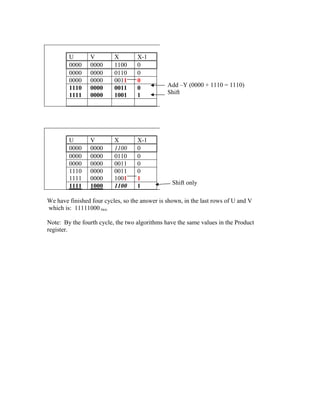
The document summarizes the Booth multiplication algorithm, which provides an efficient procedure for multiplying binary integers represented in two's complement form. It illustrates the algorithm through an example of multiplying 2 x -4. The algorithm involves making a Booth table with the multiplier and multiplicand, then examining the bits in each cycle to determine whether to add, subtract, or shift the partial product without modification according to specific rules. After four cycles representing the four bit numbers, the final product is stored in the last rows of the U and V registers.