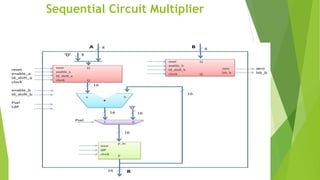
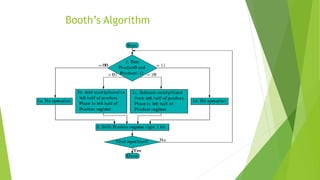
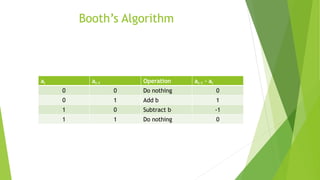
The document discusses different methods for multiplication of binary numbers, including combinational and sequential multipliers. A sequential multiplier uses one parallel adder, registers capable of shifting, and control logic. It multiplies digits through addition and shifting the registers. For signed multiplication, the multiplier and multiplicand may need to be complemented depending on their signs. Booth's algorithm can multiply signed numbers by adding or subtracting the multiplicand instead of just adding, reducing the number of operations.