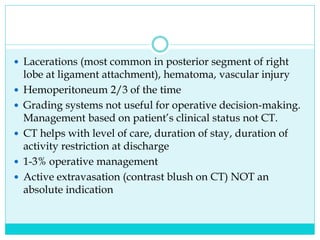
- Blunt abdominal trauma is common in children and can cause significant morbidity and mortality if not recognized.
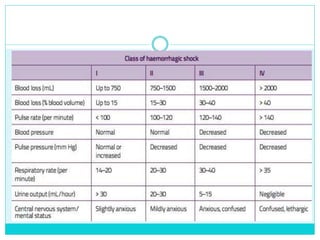
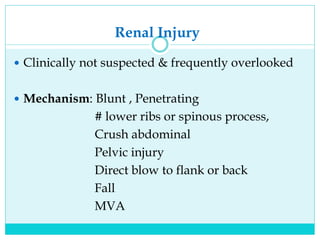
- The abdomen is more vulnerable in children due to relatively larger and more exposed solid organs as well as less muscle protection.
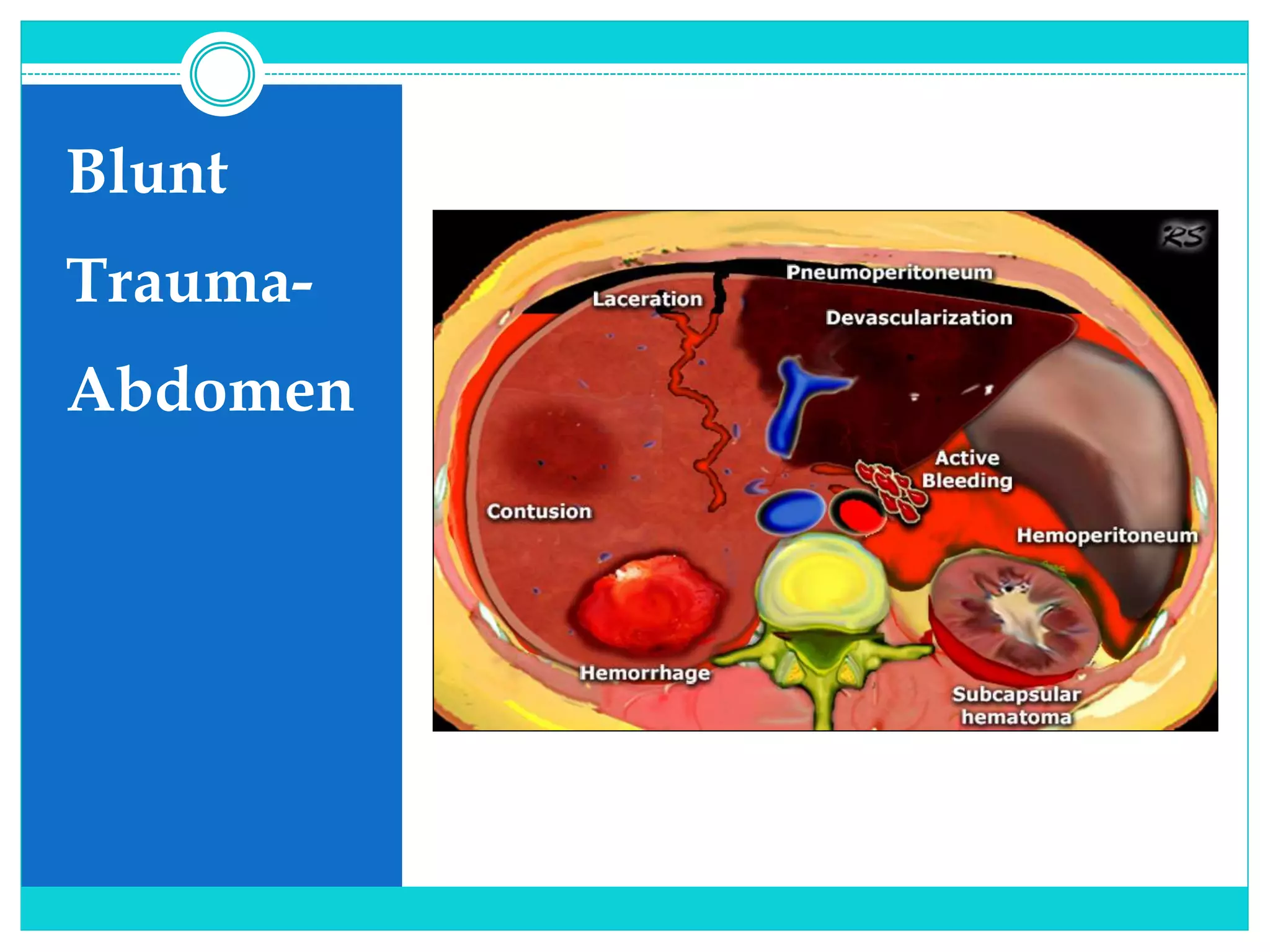
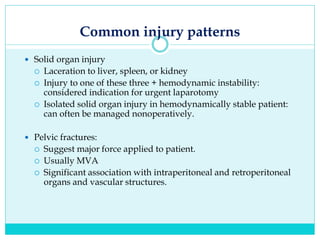
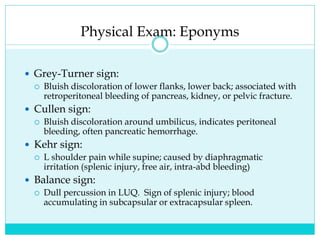
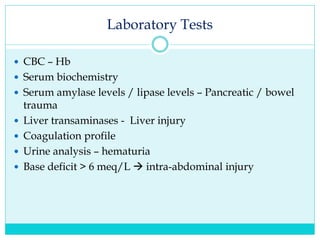
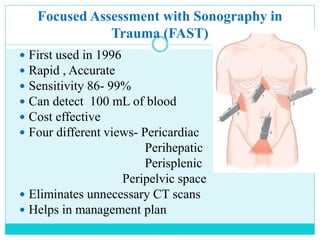
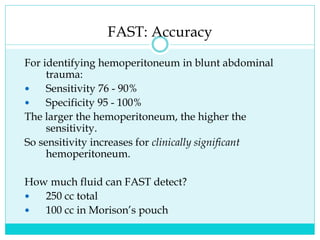
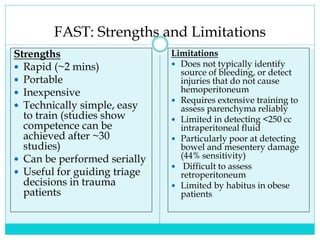
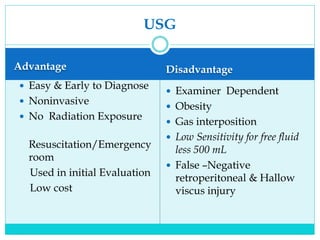
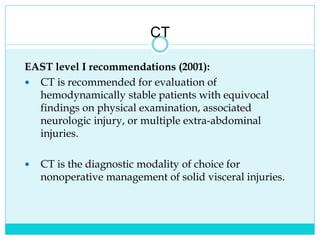
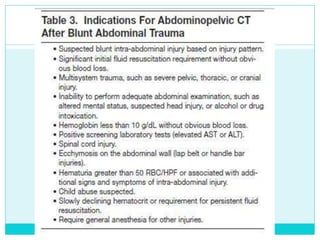
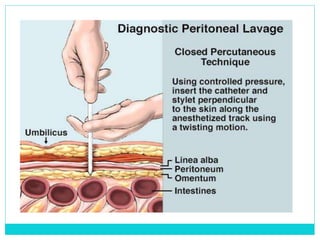
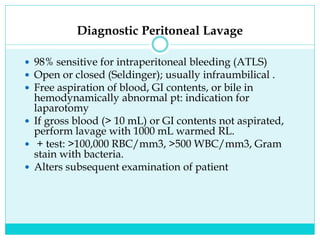
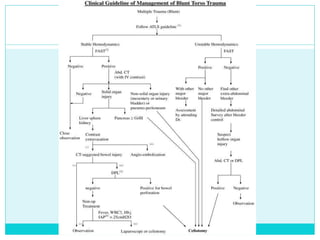
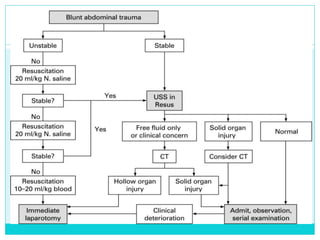
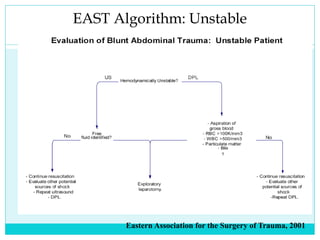
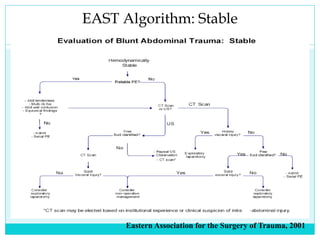
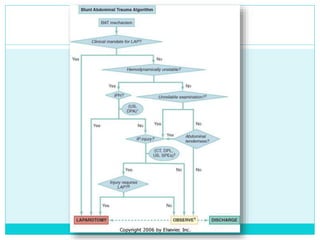
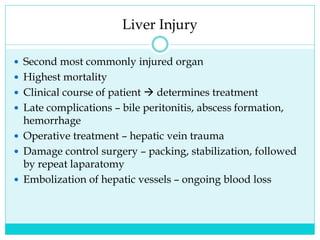
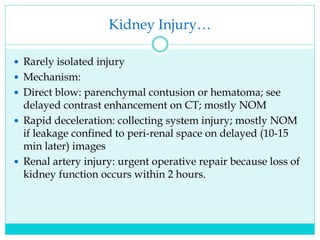
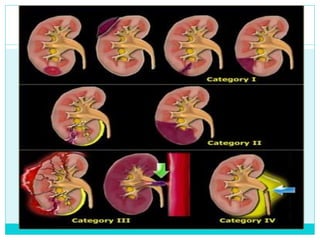
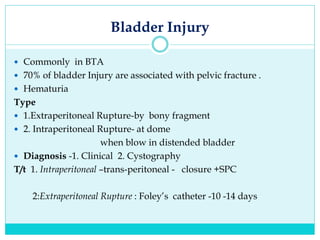
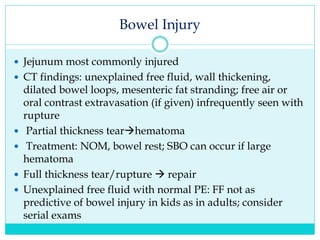
- A thorough physical exam, focused ultrasound (FAST), and CT scan are used to evaluate for injuries like lacerations to the liver, spleen, and kidneys.
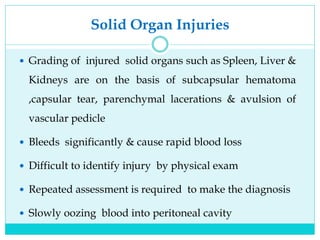
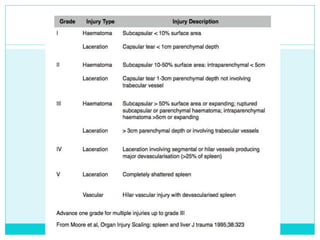
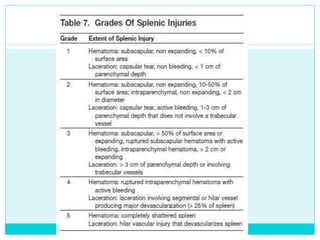
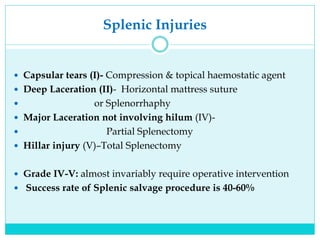
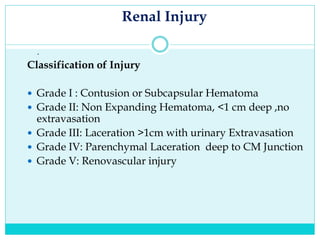
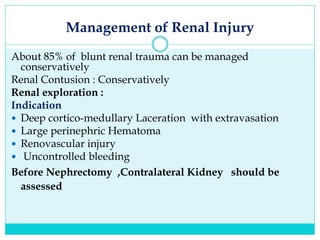
- Most solid organ injuries can be managed non-operatively if the patient is hemodynamically stable, but laparotomy may be needed for severe injuries or instability. Grading systems help determine appropriate treatment for injuries.