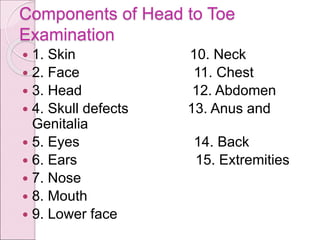
The document provides a comprehensive evaluation of newborns, defining key terms such as 'newborn', categorizing neonates by birth weight, and outlining assessment procedures during the early days of life. Key areas of focus include the timing and components of newborn assessments, danger signs, and the importance of maternal history in anticipating congenital anomalies. The document also details normal vital signs and common birth injuries and anomalies observed during initial examinations.