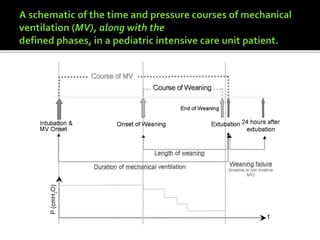
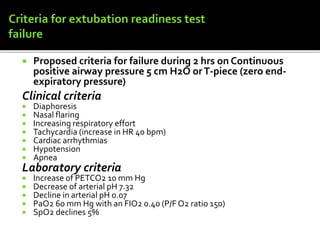
Respiratory failures are critical causes of pediatric morbidity and mortality, characterized by two types: hypoxemic and hypercapnic respiratory failures, which necessitate interventions like mechanical ventilation (MV). The weaning process from MV to spontaneous breathing is essential and must be managed carefully to prevent complications and ensure successful extubation, which requires meeting specific criteria. Factors influencing extubation success include age, oxygenation index, length of MV, and clinical indications of respiratory stability.