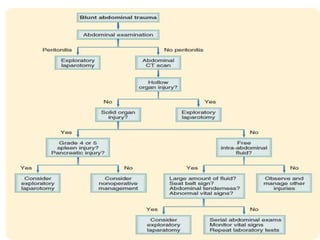
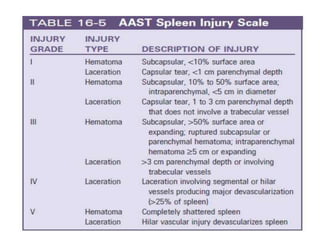
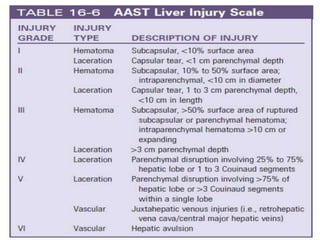
This document discusses blunt abdominal trauma (BAT). BAT is commonly caused by vehicle accidents, assaults, falls, or sports injuries. Clinical diagnosis involves a high suspicion of intra-abdominal injury based on abdominal pain, bruising, guarding, or tenderness. Assessment of hemodynamic stability is important. Investigations like FAST ultrasound or CT scan can detect free fluid or bleeding. Unstable patients may require emergent laparotomy while stable patients can be managed non-operatively with angioembolization. Treatment involves resuscitation, bleeding control through laparotomy or damage control surgery, and repair of hollow viscus injuries.