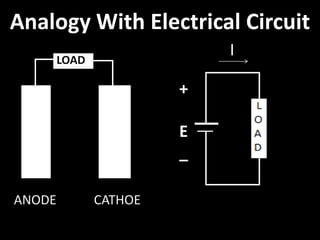
This document discusses blue energy, also known as reverse electro-dialysis, which is an emerging renewable energy source that uses the difference in salt concentration between salt water and fresh water to generate electricity. It explains the processes of reverse osmosis and reverse electro-dialysis to produce energy. Parameters from an existing blue energy plant in the Netherlands are provided, showing it can generate 250kW of power. Advantages include being renewable, pollution-free, and able to generate power continuously. Disadvantages include high initial costs and maintaining membranes. The future prospects of blue energy reducing costs and providing 40% of worldwide energy demand are mentioned.