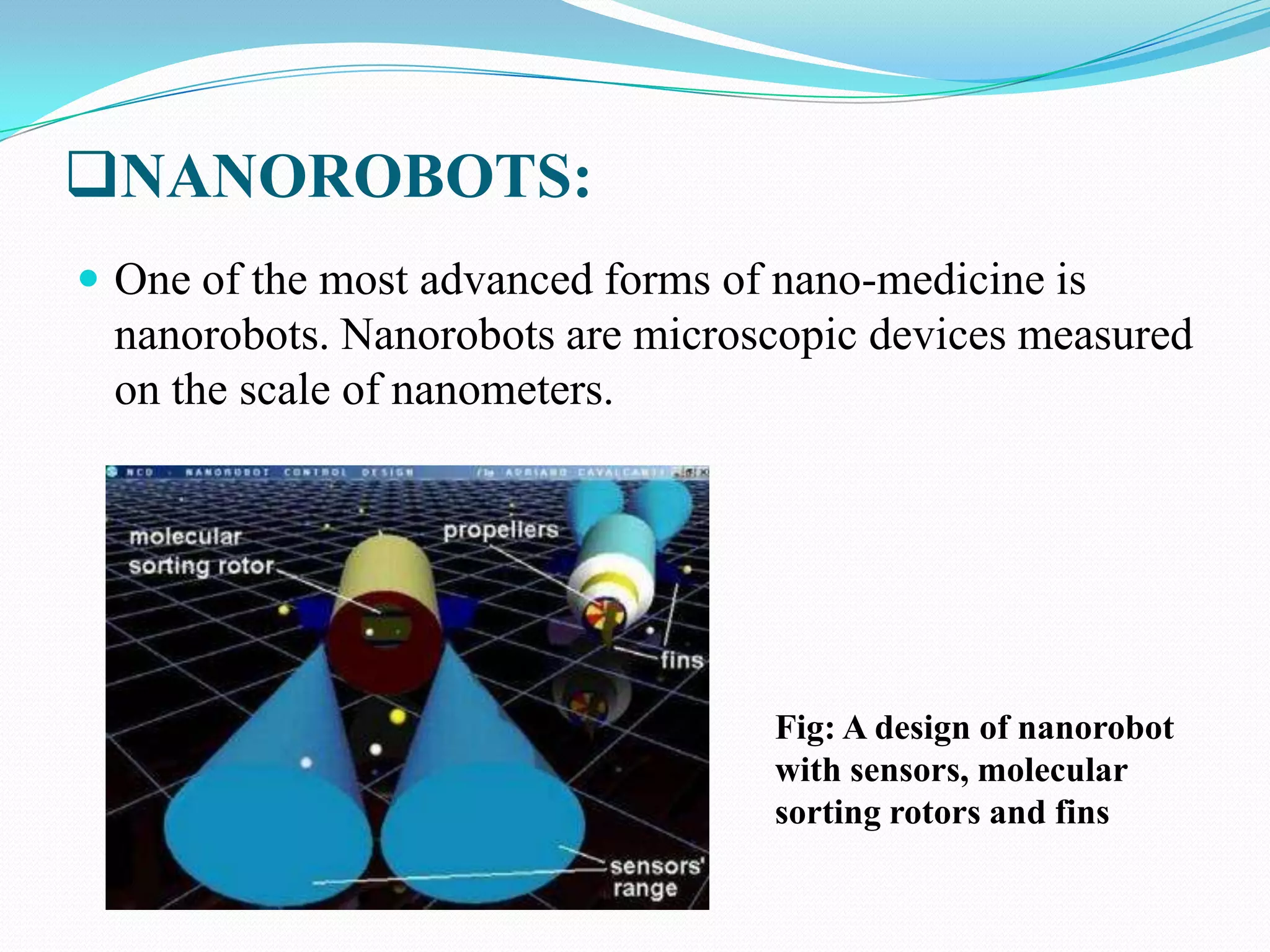
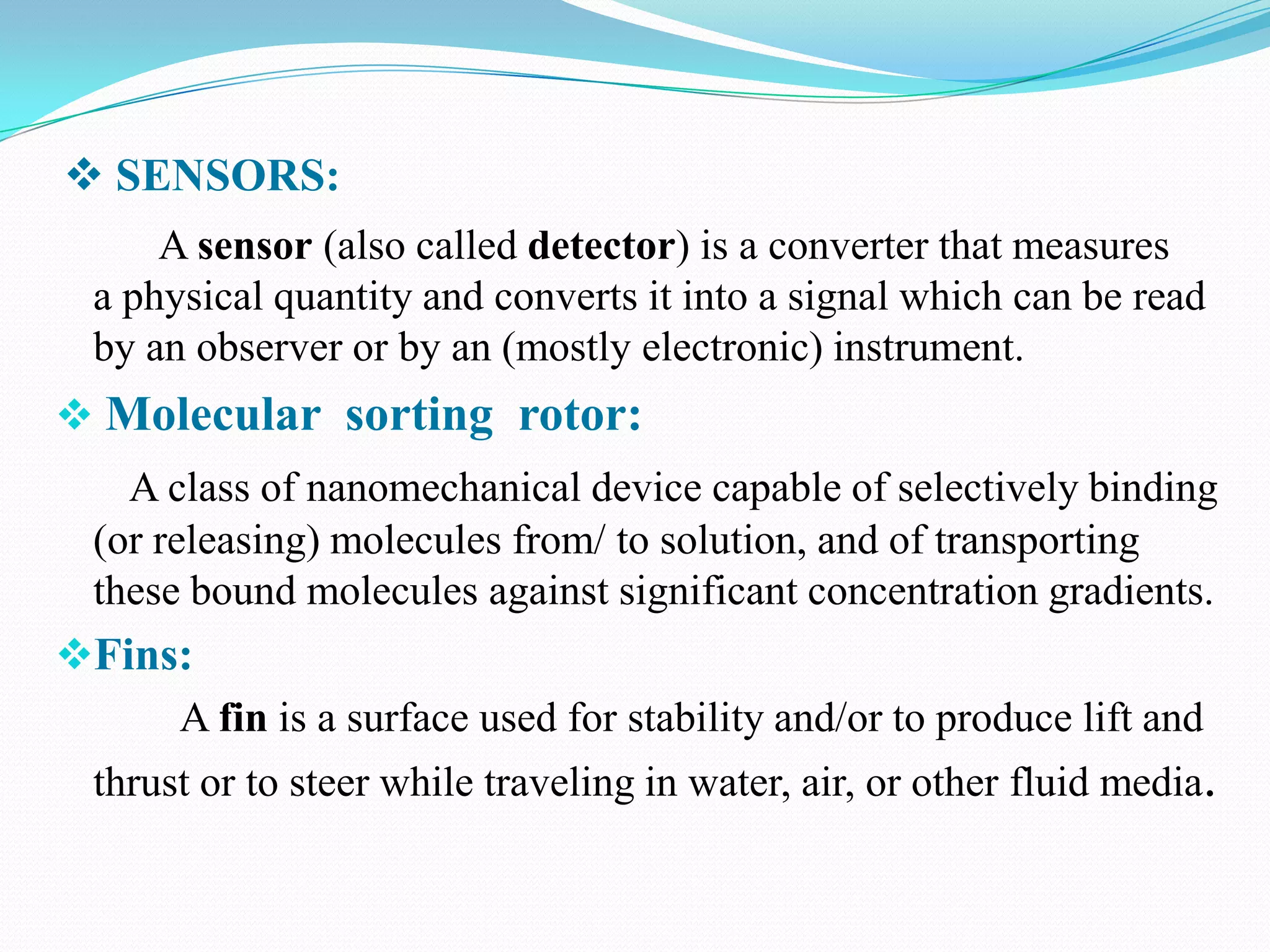
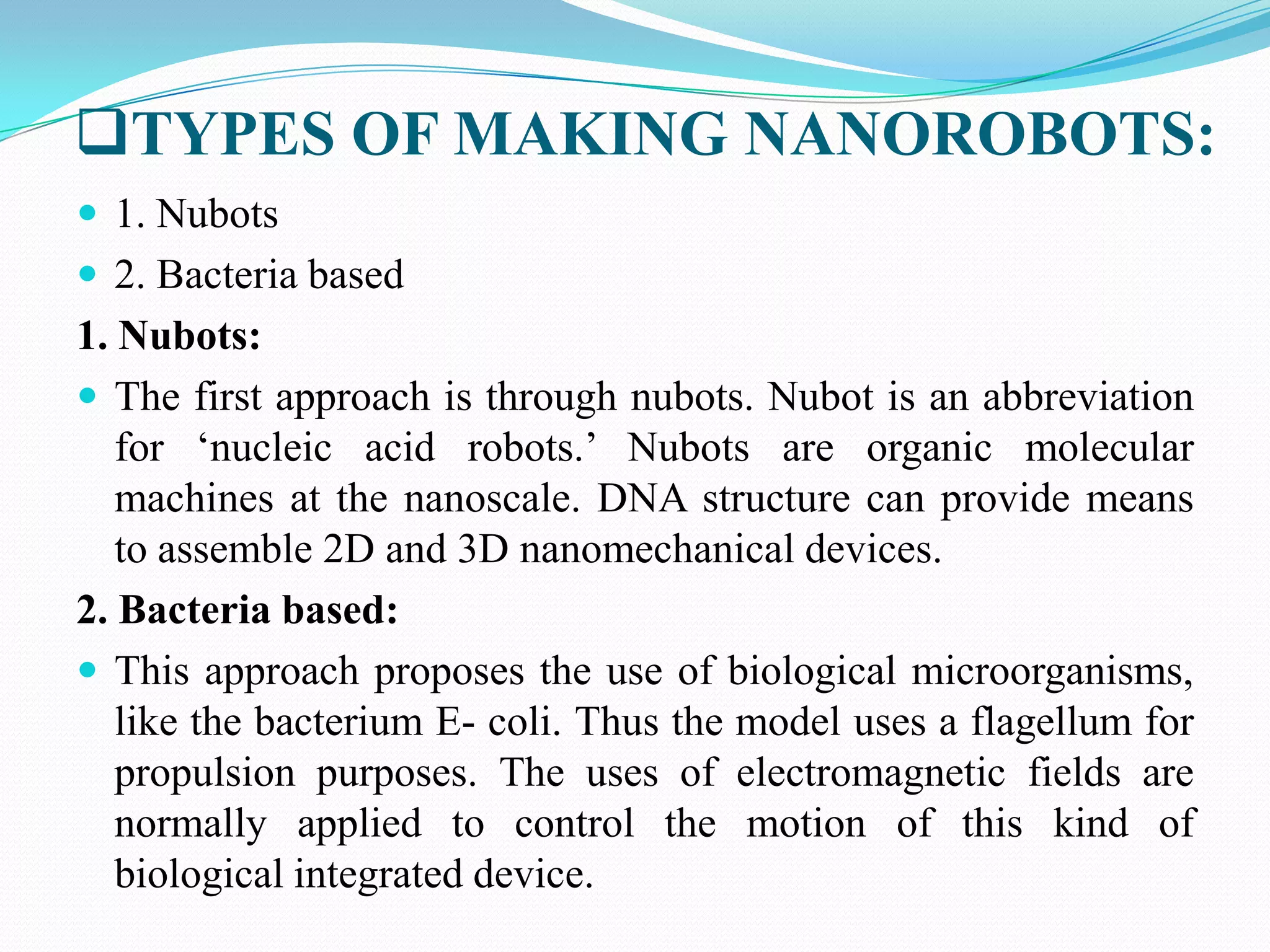
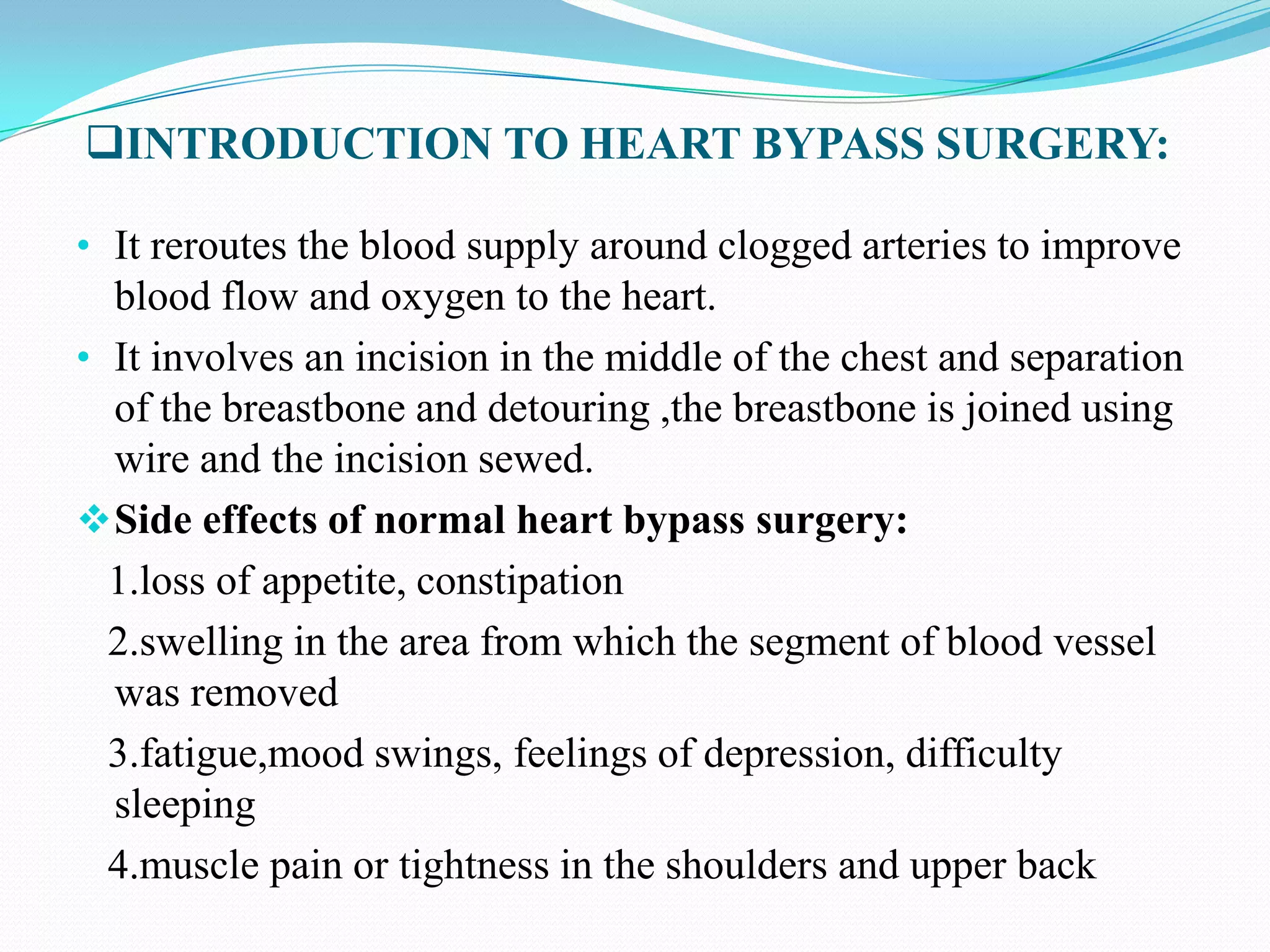
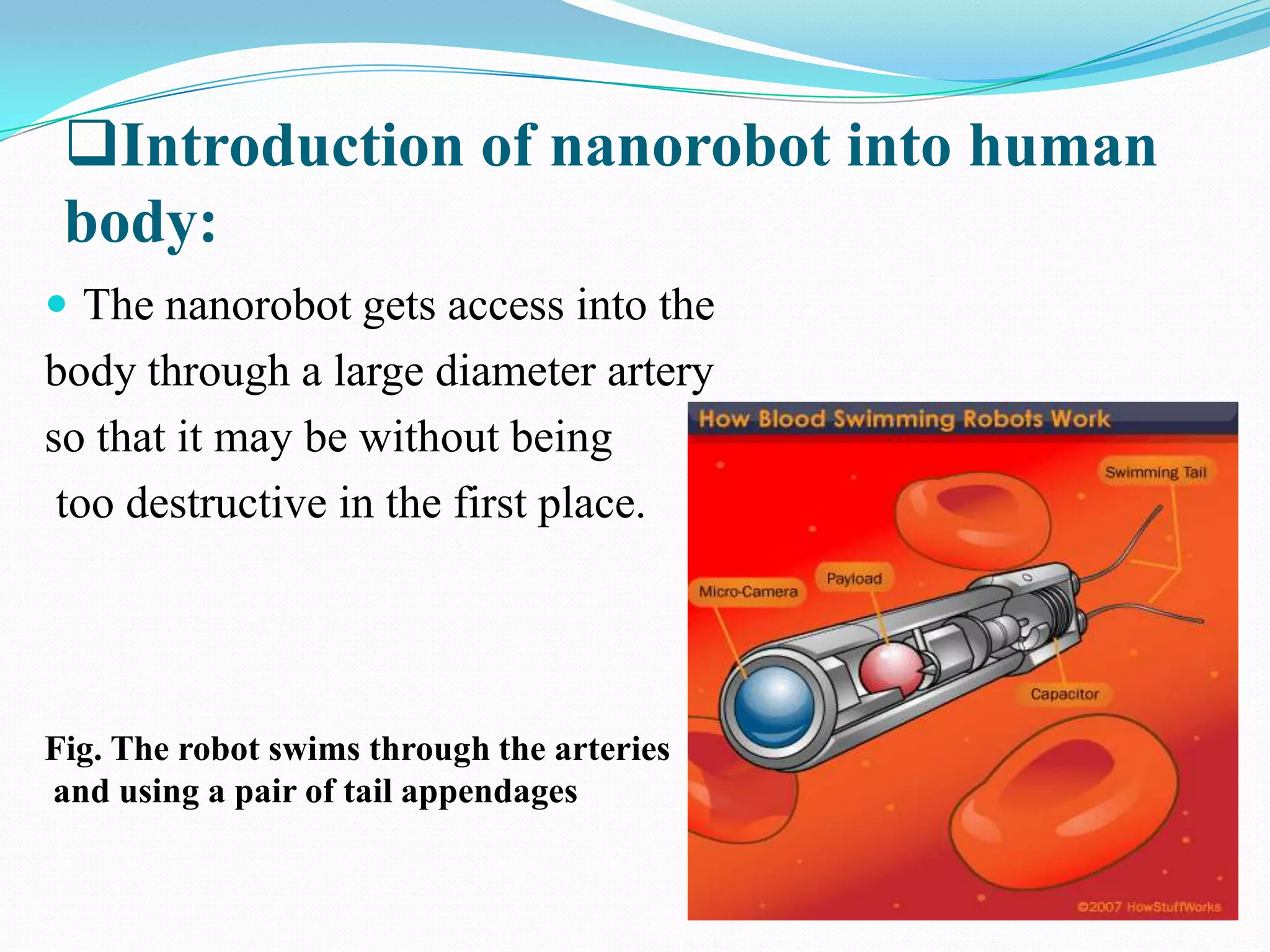
Nanorobotics is the emerging field of engineering nanorobots, which are robotic devices between 0.1-10 micrometers that are constructed of nanoscale or molecular components. Nanorobots could have applications in medicine such as performing surgery. One potential application is using a nanorobot to remove plaque from arteries and perform heart bypass surgery. The nanorobot would navigate through the bloodstream using sensors and propellers. It could identify plaque using temperature sensors and cameras. The nanorobot would then remove the plaque using a rotating needle. It would be powered by a nuclear power source and guided out of the body by surgery to remove it after completing the procedure. This could allow bypass surgery to be performed without major inc








![REFERENCES:
1. Nocks, Lisa (2007). The robot : the life story of a technology. Westport, CT: Greenwood
Publishing Group
2. Nanorobot “International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences”.
[Online] Available: http://www.ijpbs.net/51.pdf
3. "What Nanobots Are Made Out Of." How Nanorobots Are Made.
[Online] Available: http://nanogloss.com/nanobots/how-nanorobots-are-made/
4. (2011,April 12). H.Wang. "Basic Properties of Diamond." Diamond Blade Select.
[Online] Available: http://www.diamondbladeselect.com/knowledge/basic-properties-ofdiamond/
5. (2012, February 22). J. Malone."Advanced Nanobots Deliver Targeted Drugs." COSMOS.
[Online]Available:http://www.cosmosmagazine.com/news/5321/dna-nanobots-delivertargetted-drugs
6. (2009, January 7). "Nanorobots to Fight Cancer, Diagnose Disease - Health - CBC
News." CBC.ca - Canadian News Sports Entertainment Kids Docs Radio TV.
[Online]Available:http://www.cbc.ca/news/health/story/2009/01/07/nanomedicine.html
7. S. Hede and N. Huilgol.(2006) ""Nano": The New Nemesis of Cancer ." Journal of Cancer
Research and Therapeutics: Free Full Text Articles from JCRT, India.
[Online]Available:http://www.cancerjournal.net/article.asp?issn=09731482;year=2006;volume=2;issue=4;spage=186;epage=195;aulast=Hede](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nanorobotics-131120073826-phpapp01/75/A-seminar-on-Nanorobotics-19-2048.jpg)
