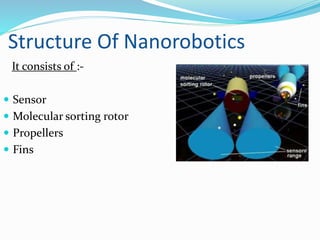
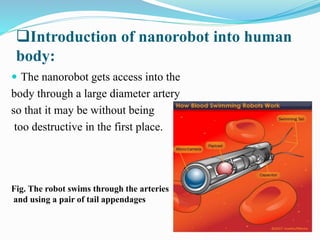
The document discusses the fields of robotics and nanotechnology, highlighting the emergence of nanorobotics and its potential applications, particularly in medical sciences such as heart bypass surgery. It covers the history, design, and construction of nanorobots, including their components and types, as well as potential benefits and disadvantages. The conclusion emphasizes nanorobotics as a safer and more efficient alternative to traditional surgical methods.