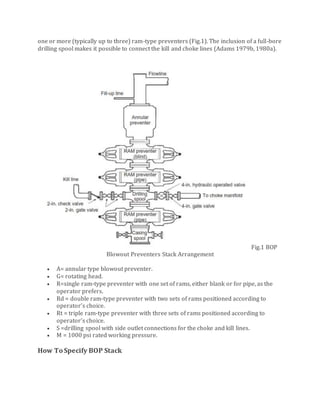
This document discusses blowout preventers (BOP) stack components and types, focusing on their classification, specifications, and operational requirements in drilling. It outlines various BOP types, including annular and ram-type preventers, along with their functions, maintenance, and safety standards for different rig types. Additionally, it provides recommendations for stack requirements based on pressure ratings and operational contexts, emphasizing safety and efficiency in blowout prevention.