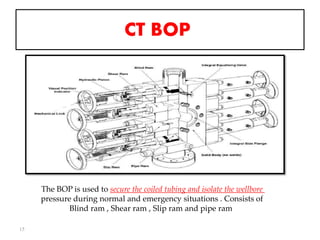
This document discusses well intervention using coiled tubing. It defines coiled tubing and its main components, which include an injector head, coiled tubing reel, control unit, power pack unit, and bottom-hole assembly. Coiled tubing can be used for various applications like wellbore cleanout, milling, logging, perforating, drilling deviated wells, fluid conveyance, and tool conveyance. It has advantages over conventional drilling like not requiring connections and allowing faster tripping in and out. However, coiled tubing also has disadvantages like fatigue life limits and reduced bore diameter.