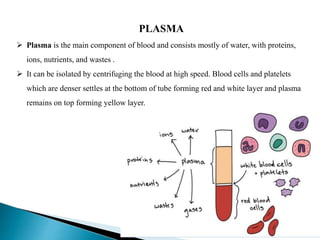
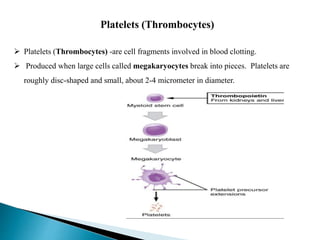
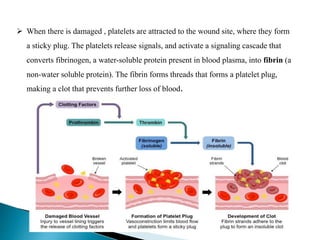
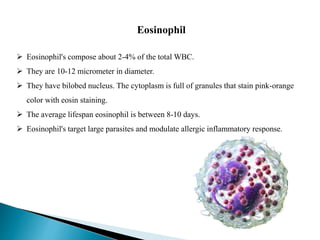
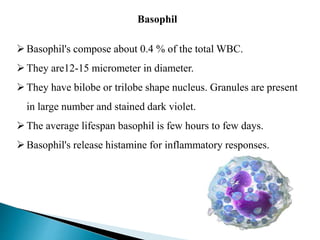
Blood contains plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is mostly water containing proteins, ions, nutrients, and waste. Red blood cells carry oxygen to tissues and carbon dioxide back to the lungs using hemoglobin. Platelets form blood clots to prevent blood loss from damaged vessels. White blood cells include neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils which fight infection and disease. Each blood component has specialized functions in transporting substances and protecting the body.