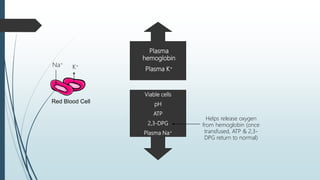
This document discusses the storage and uses of blood components. It defines blood products and lists the main blood components as red blood cells, platelets, granulocytes, fresh frozen plasma, and cryoprecipitate. It provides details on collection methods, separation techniques, storage conditions, and recommended uses for each component in treating conditions like blood loss, bleeding disorders, and bone marrow transplantation. The document emphasizes the importance of using only the required blood component for a condition to conserve this scarce medical resource.