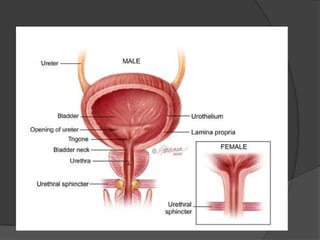
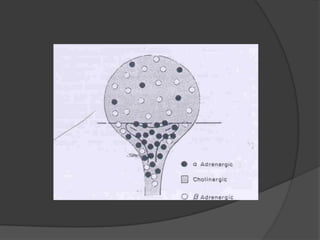
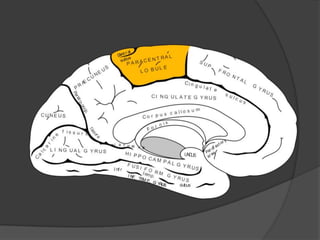
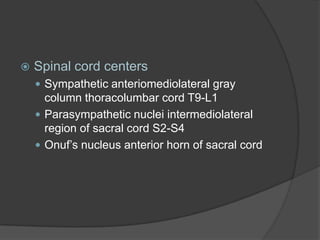
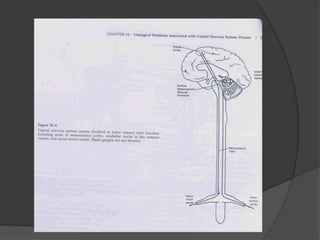
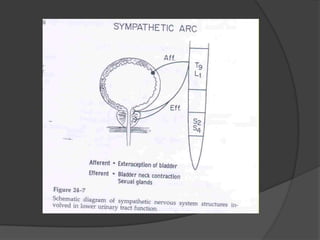
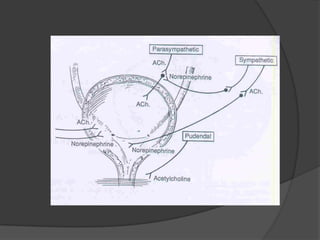
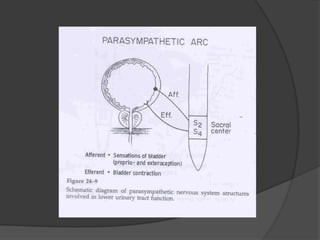
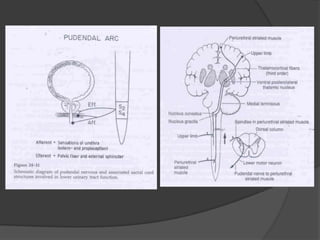
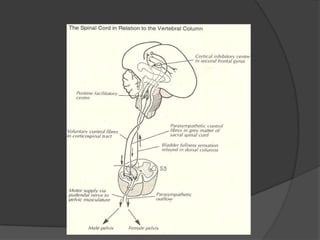
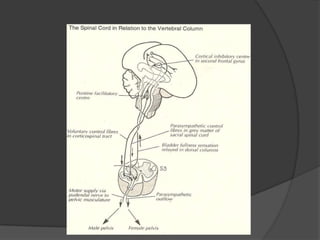
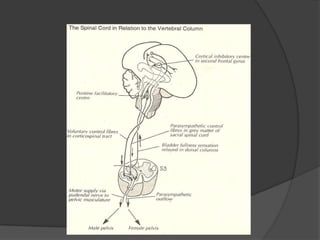
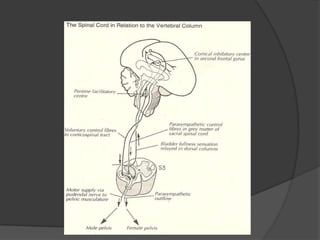
This document provides an overview of neurourological anatomy and physiology. It discusses the central nervous system centers that control bladder function, including the pons, cortex, basal ganglia and cerebellum, as well as spinal cord centers. It describes the arcs and loops involved in bladder control, including supra spinal, sympathetic, parasympathetic and pudendal arcs and loops. It also covers spinal tracts, basic concepts of neurourological function, reflexes, types of neurogenic bladder dysfunction, and pharmacological management options.