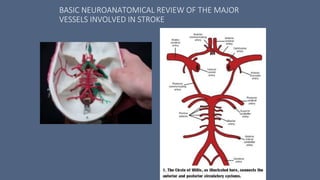
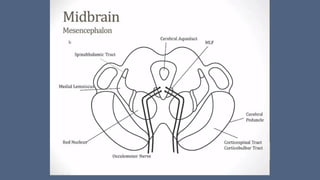
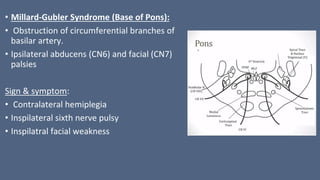
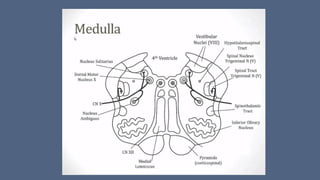
1. Stroke is defined as a nontraumatic brain injury caused by occlusion or rupture of cerebral blood vessels that results in sudden neurological deficits.
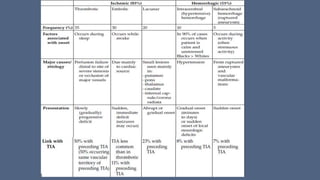
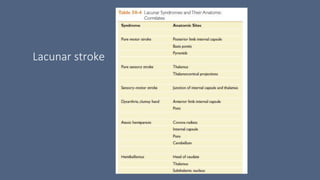
2. The most common types of stroke are ischemic (85%) and hemorrhagic (15%). Ischemic strokes are further classified as thrombotic, embolic, or lacunar.
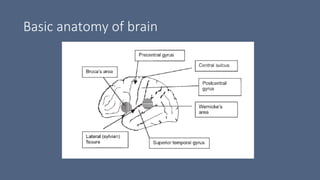
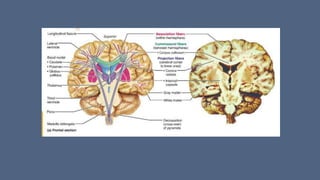
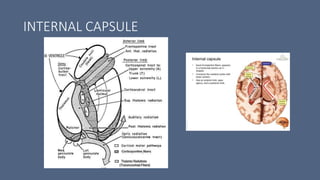
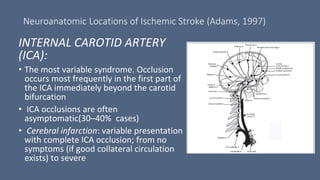
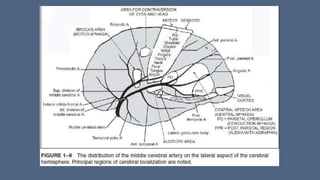
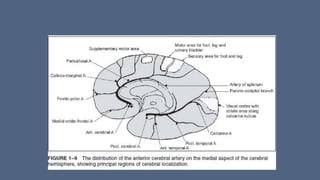
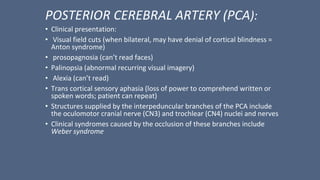
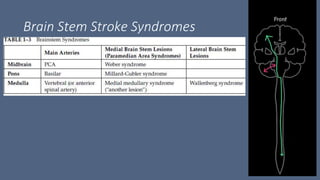
3. Major risk factors for stroke include hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, smoking, and older age. Location of brain injury determines the specific neurological symptoms, such as deficits on one side of the body for middle cerebral artery strokes.