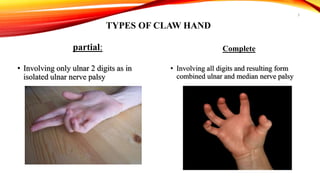
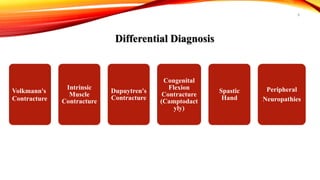
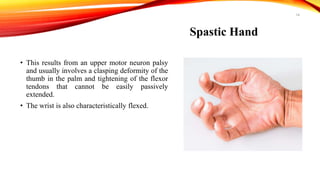
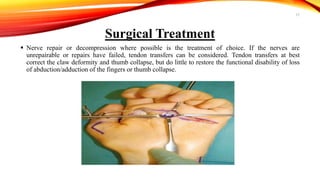
Claw hand is a deformity caused by issues with the ulnar and median nerves, resulting in an abnormal hand position where the 4th and 5th fingers are extended at the metacarpophalangeal joints and flexed at the interphalangeal joints. It can be caused by various factors, including congenital defects, nerve injuries, and underlying medical conditions, with symptoms leading to functional disabilities in hand movement. Management includes surgical interventions, postoperative care, and preventative exercises to maintain finger function.