1. The document discusses the neurologic control of the urinary system, including the pathways involved in storage and voiding of urine and the effects of lesions along these pathways.
2. It describes how lesions in different areas can result in conditions like urinary frequency, retention, or obstructed voiding and discusses the clinical presentations of different neurogenic bladder disorders.
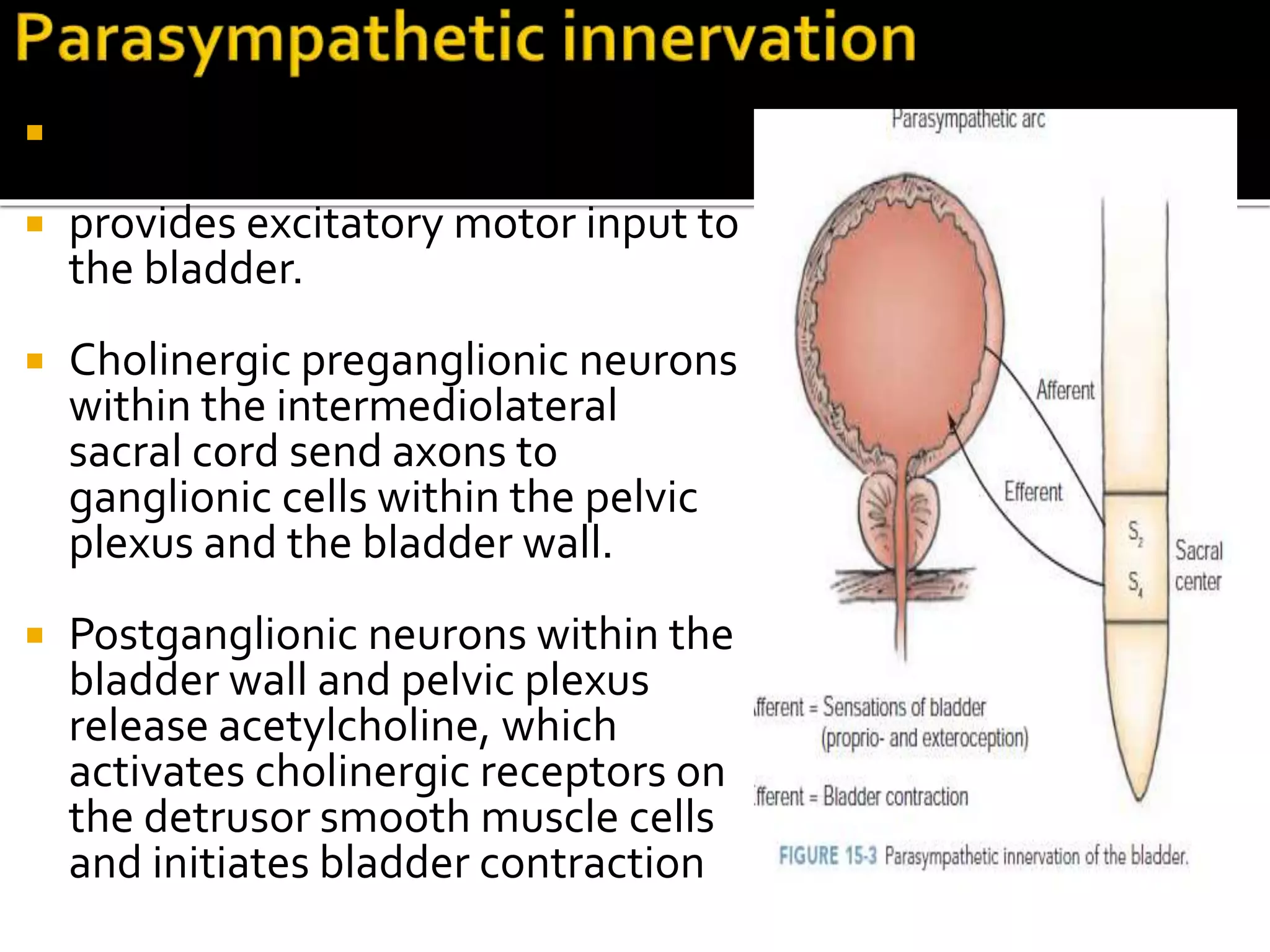
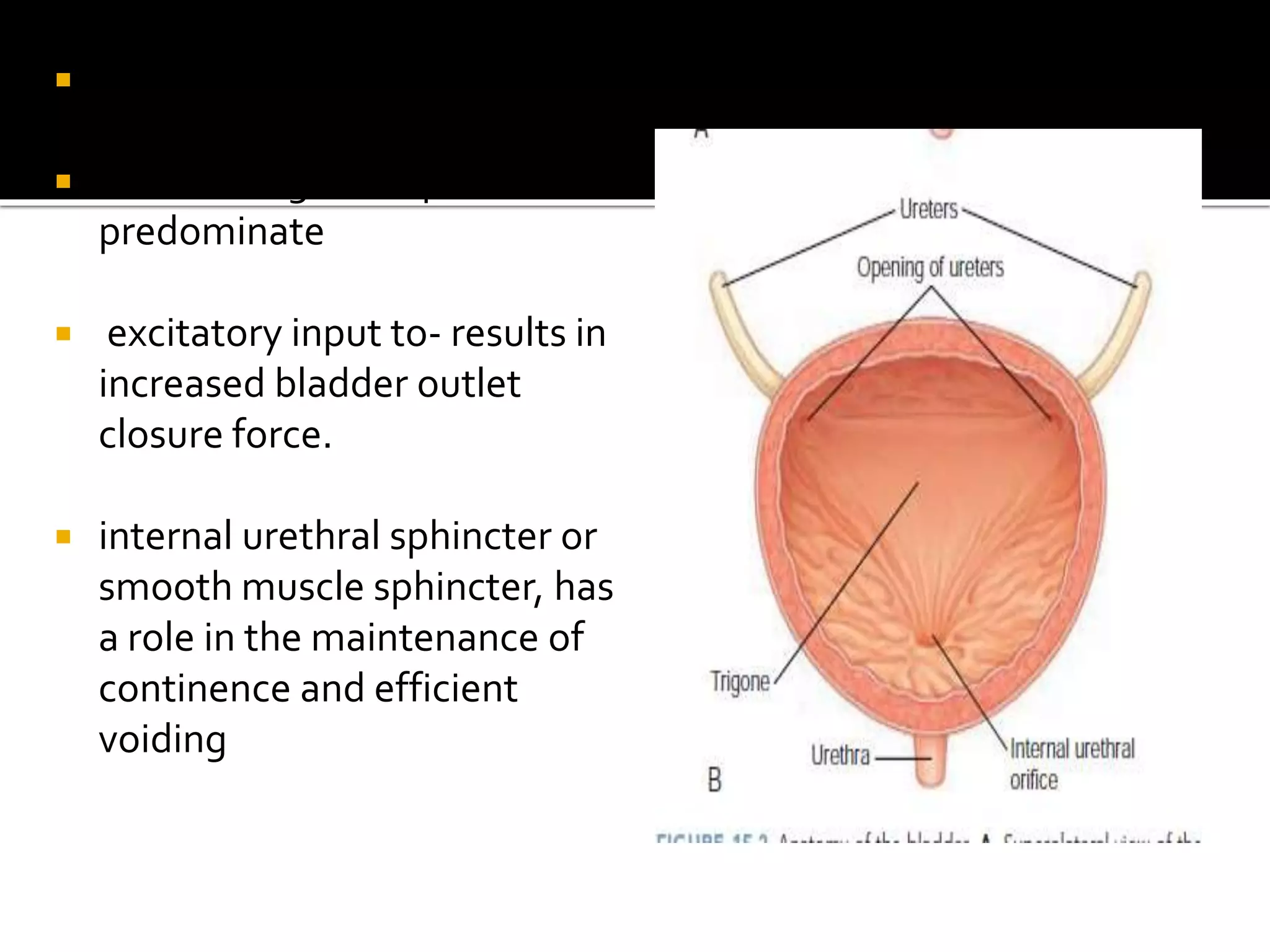
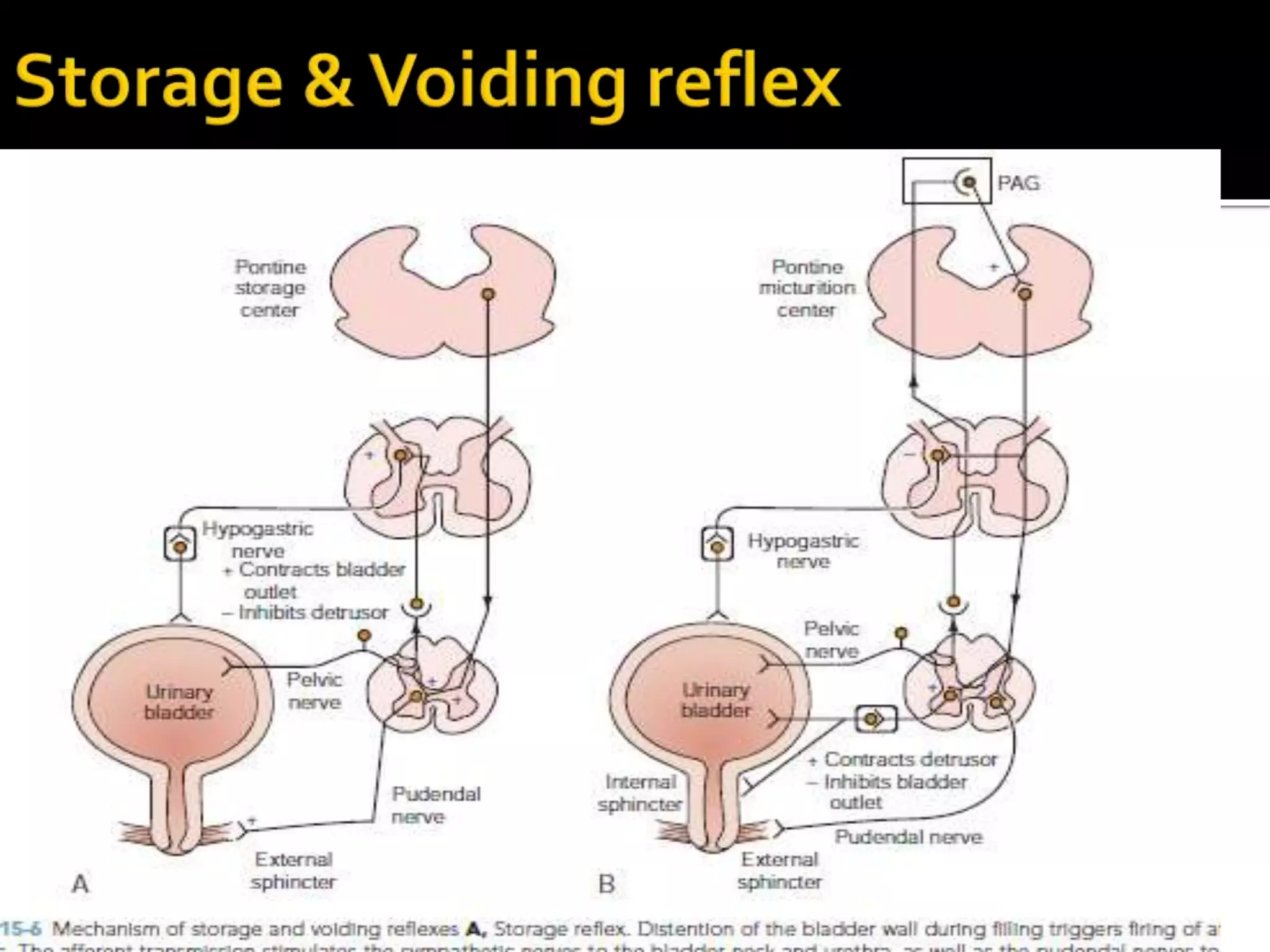
3. The pathways discussed include the cerebral, cord, urethral, and detrusor reflex loops which coordinate the bladder and sphincter during the storage and voiding phases of micturition.