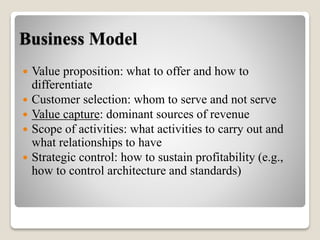
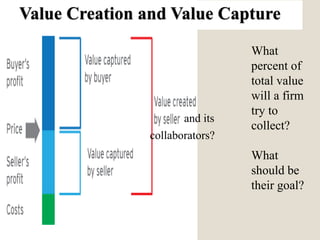
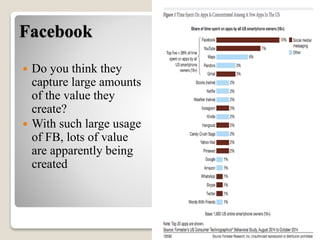
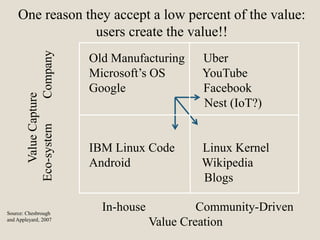
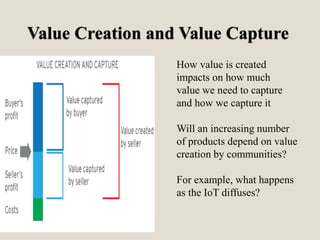
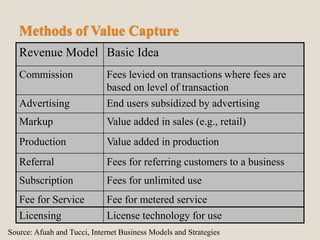
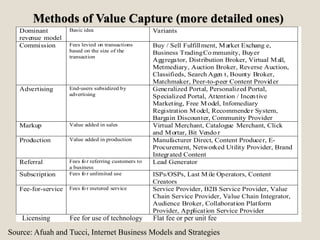
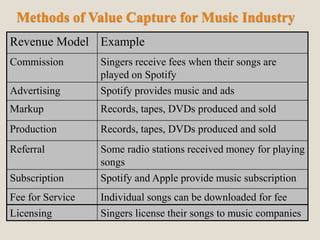
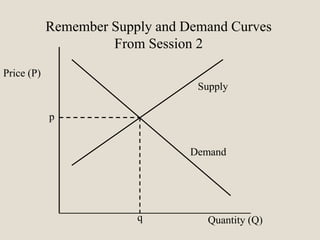
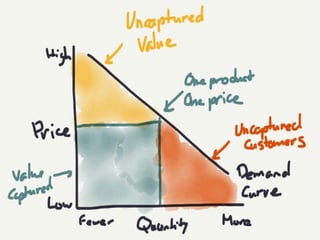
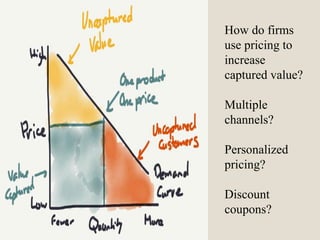
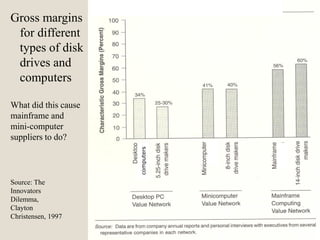
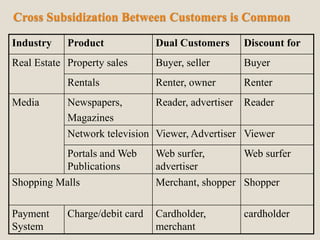
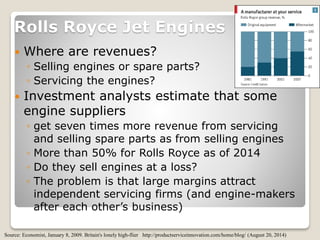
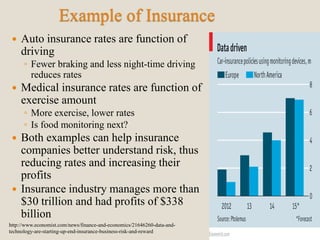
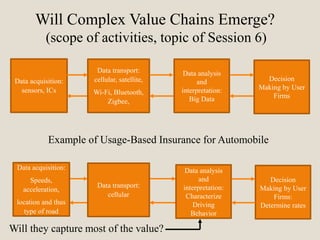
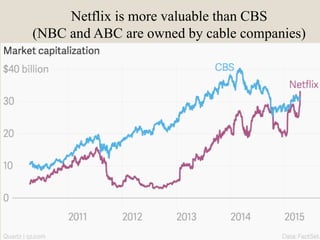
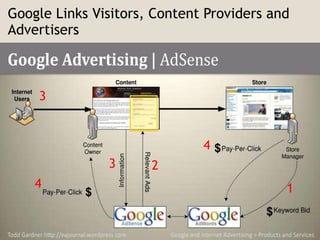
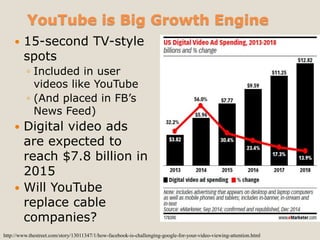
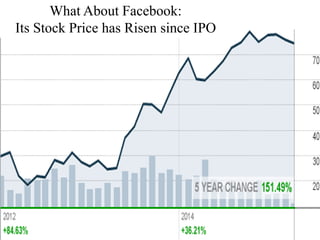
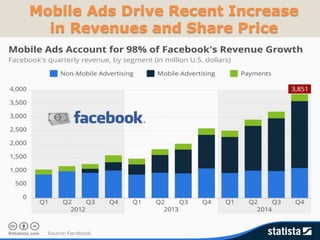
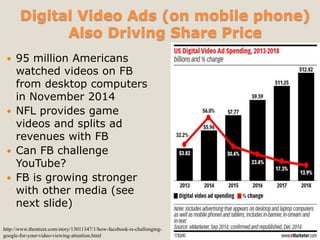
The document discusses various methods of value capture within business models for high-tech products, focusing on how companies differentiate their offerings, select customers, and sustain profitability. It highlights examples from industries such as computing, transportation, and the internet of things, illustrating shifts in revenue models like service contracts over traditional sales. The importance of data utilization and cooperation between sellers and buyers is emphasized, especially in the context of emerging technologies and markets.