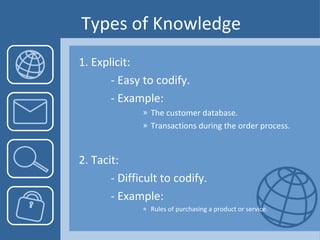
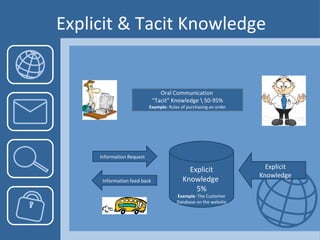
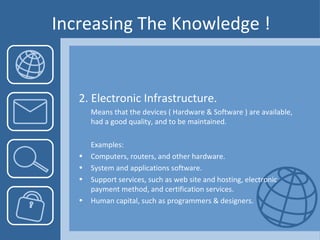
This document discusses the importance of knowledge management for e-commerce. It defines e-commerce and knowledge management, and explains how KM helps e-commerce businesses by allowing them to react quickly to opportunities, ensure successful partnerships, and maximize performance. It outlines different types of knowledge and discusses strategies for increasing knowledge, such as improving infrastructure and social engagement. Overall, the document argues that applying a knowledge management approach is crucial for e-commerce companies to gain competitive advantages.