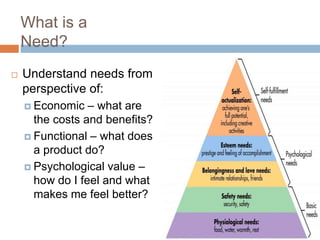
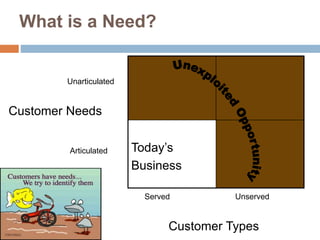
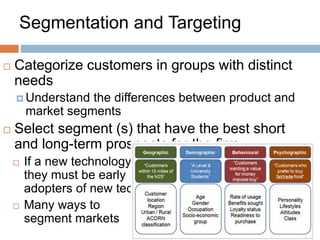
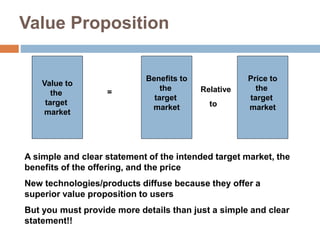
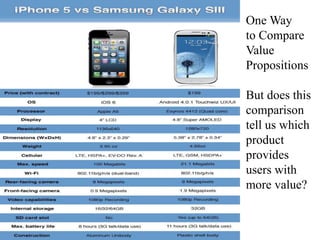
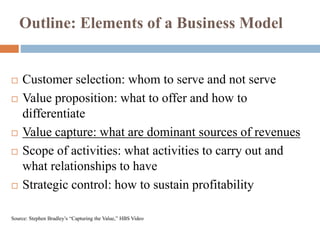
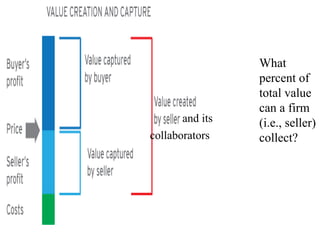
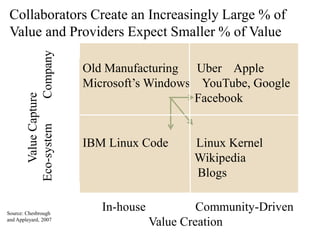
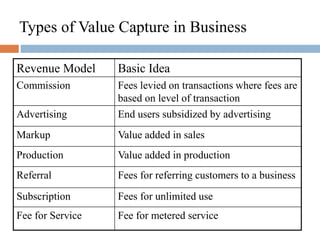
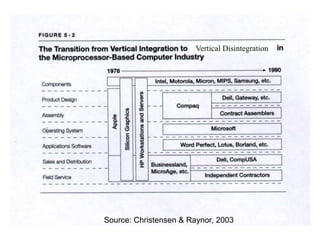
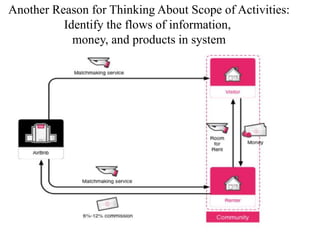
This document discusses business models for high-tech products, emphasizing the importance of establishing new rules for emerging industries to enhance product success. It outlines key elements such as customer selection, value proposition, revenue capture, scope of activities, and strategic control, which are crucial for firms to achieve profitability and competitive advantage. Additionally, it underscores the necessity of innovation in value capture methods and emphasizes collaboration with multiple stakeholders to optimize market entry and long-term sustainability.