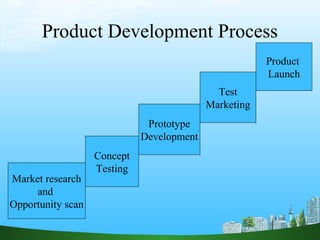
The document discusses the process of new product development, which includes market research, concept testing, prototype development, market testing, and product launch. It emphasizes the importance of market research to understand customer needs and identify opportunities. The development process then progresses through building prototypes, testing concepts with customers, and launching the new product in the market.