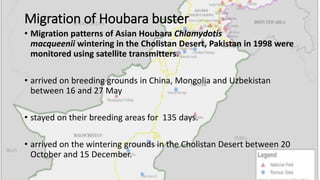
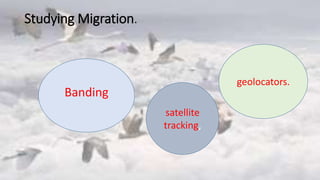
Birds migrate for various reasons including seeking food, avoiding predators, and responding to seasonal changes. There are different types of bird migration including longitudinal, altitudinal, and partial migrations. Birds have developed adaptations for migration such as morphological features, behavioral modifications, specialized moult cycles, and navigation abilities. Many birds migrate along global flyways like the Africa-Eurasia, East Asia-Australasia, and Americas flyways. In Pakistan, birds migrate through the Indus flyway, and the houbara bustard undertakes long distance migration from Central Asia to Pakistan each winter. Threats to migratory birds include habitat destruction, hunting, fishing, grazing, poverty, and lack of awareness.