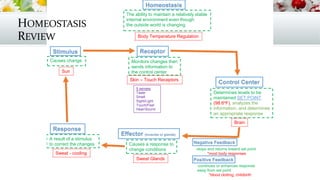
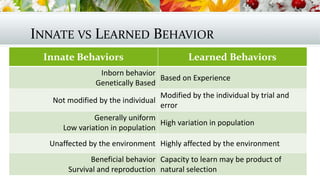
This document discusses animal behavior and how it is influenced by both innate and learned responses. It defines behavior as a response to a stimulus and explains that behavior helps organisms maintain homeostasis to survive and reproduce. The types of stimuli that can trigger behaviors include internal cues like hunger or pain, as well as external cues from predators, mates, or environmental changes. Sensory receptors detect these stimuli and activate the nervous system. Behaviors can be innate or learned through various processes like habituation, observational learning, classical and operant conditioning, play, and insight learning. Both innate behaviors like migration and learned behaviors like language are described.