- Biotic interactions include predator-prey relationships, plant-herbivore relationships, competition, and symbiosis. Abiotic interactions involve interactions between organisms and environmental factors like temperature, light, and nutrients.
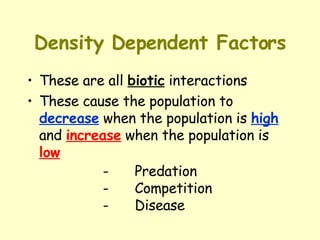
- Density-dependent factors like predation and competition cause populations to decrease when densities are high and increase when densities are low. Density-independent factors like fires and floods impact populations independently of their densities.
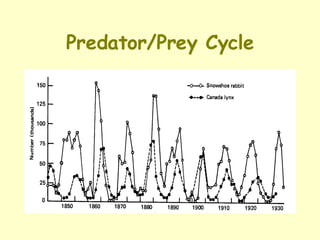
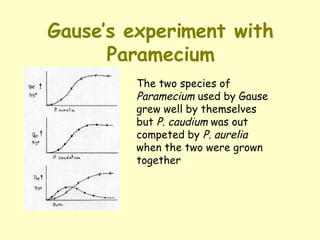
- Predator-prey relationships can follow stable, cyclical, erratic, or extinction patterns depending on factors like carrying capacity and reproduction rates of both species. Predators benefit from food while prey benefit from reduced competition.










![The Role of Predators in Maintaining Diversity in Ecosystems When different species are competing for the same resources, one will succeed at the expense of another The weaker species will be lost from the habitat [COMPETITIVE EXCLUSION] If, however, predation reduces the numbers of strong competing species, the weaker species have more of a survival chance This increases the DIVERSITY OF THE ECOSYSTEM . The more diverse an ecosystem the more stable it becomes, i.e. tends towards a climax community](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biotic-interactions-1201458262406348-4/85/Biotic-Interactions-14-320.jpg)






![Red, black and yellow are common colours and are called aposematic colours (meaning ‘away signal’) Many individual share the same pattern [ convergent evolution ] This prevents young from having to try many combinations to learn all of the animals not to eat This convergent evolution is a form of mimicry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biotic-interactions-1201458262406348-4/85/Biotic-Interactions-21-320.jpg)

















![These invasive, non-native species are a major threat to the environment because they ... can change an entire habitat, placing ecosystems at risk crowd out or replace native species that are beneficial to a habitat damage human enterprise, such as fisheries, costing the economy millions of dollars Other examples: The zebra mussel, accidentally brought to the United States from southern Russia, transforms aquatic habitats by filtering prodigious amounts of water (thereby lowering densities of planktonic organisms) and settling in dense masses over vast areas. At least thirty freshwater mussel species are threatened with extinction by the zebra mussel [HANDOUT / RESEARCH]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biotic-interactions-1201458262406348-4/85/Biotic-Interactions-42-320.jpg)
