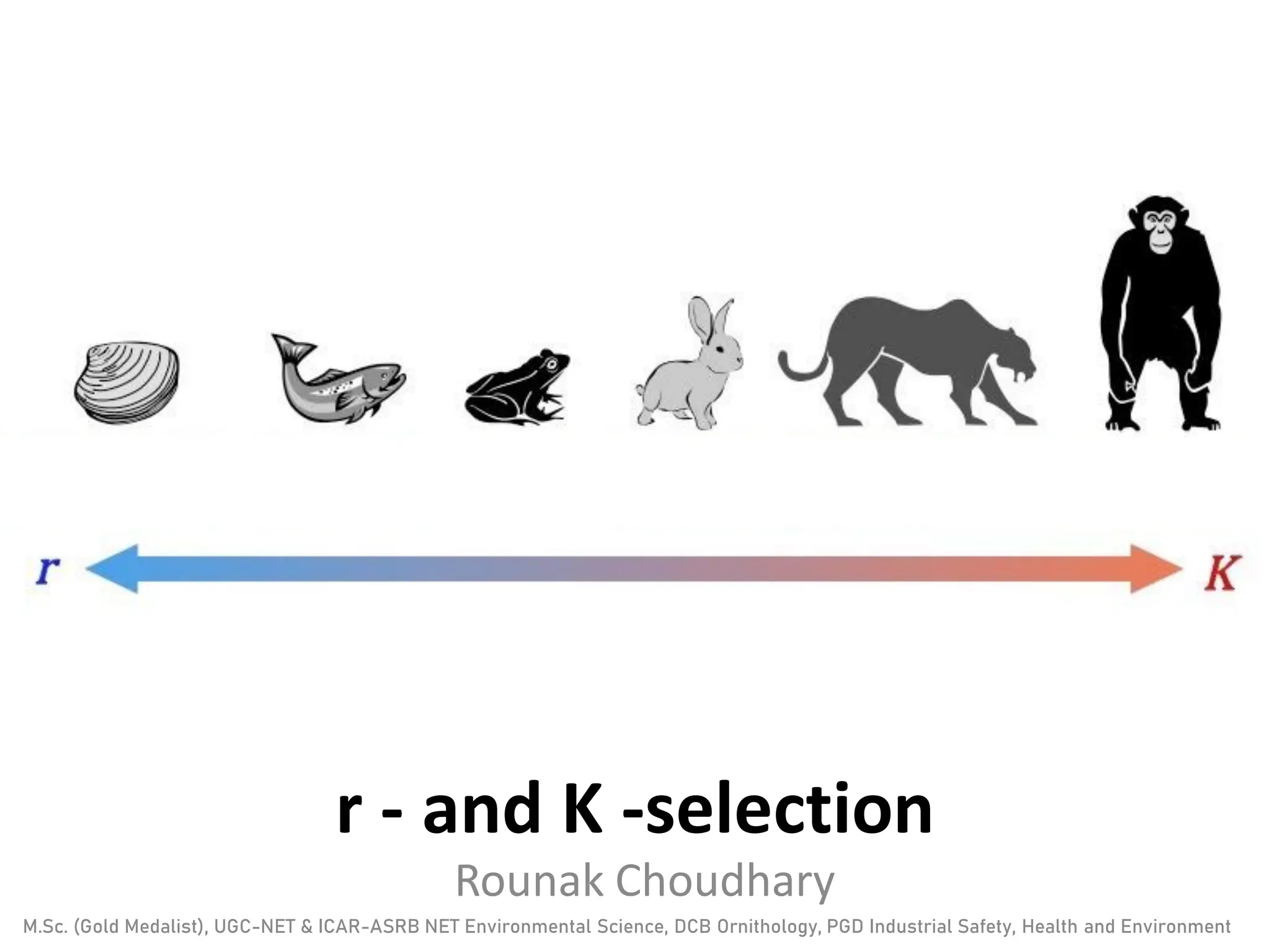
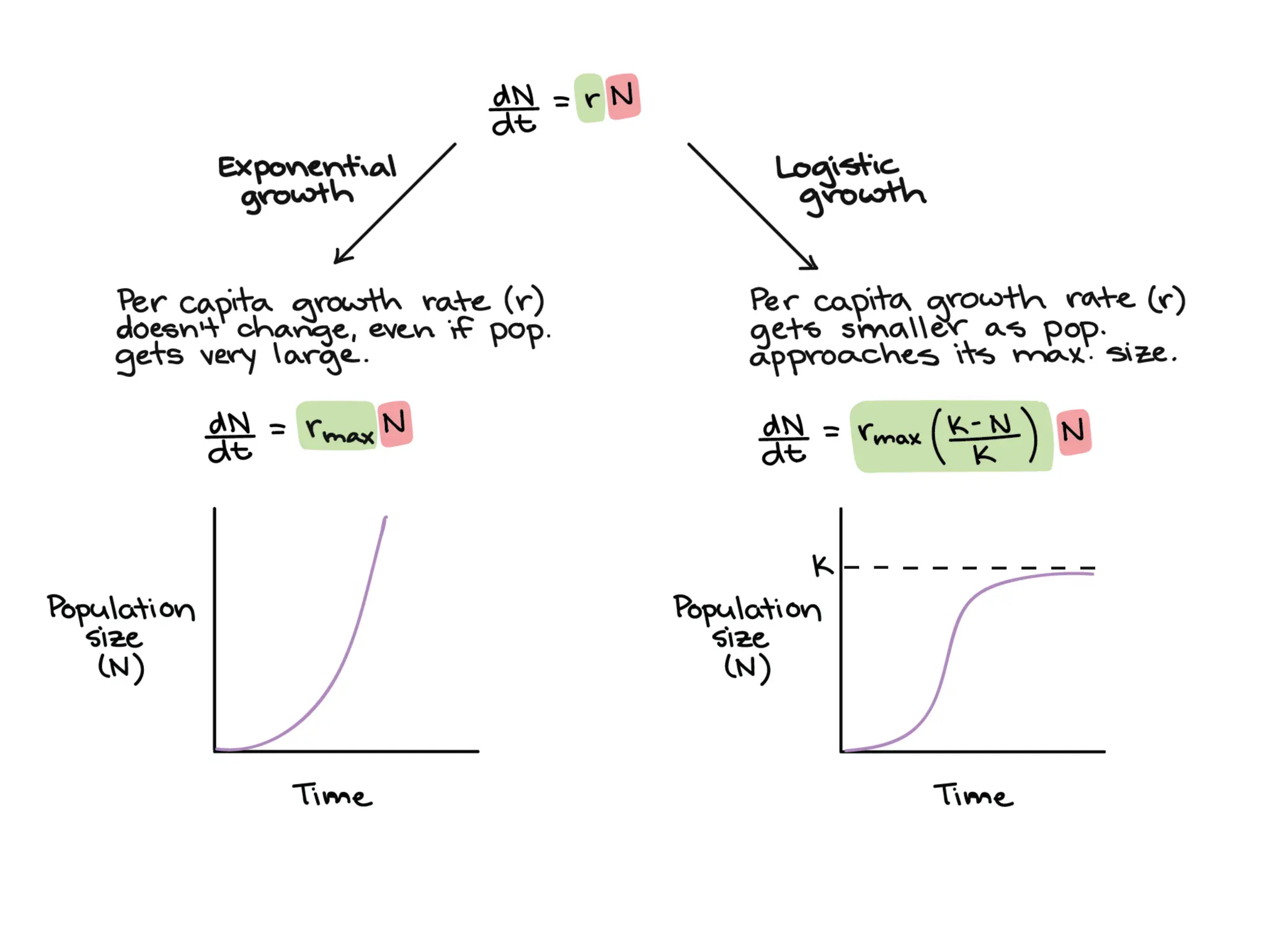
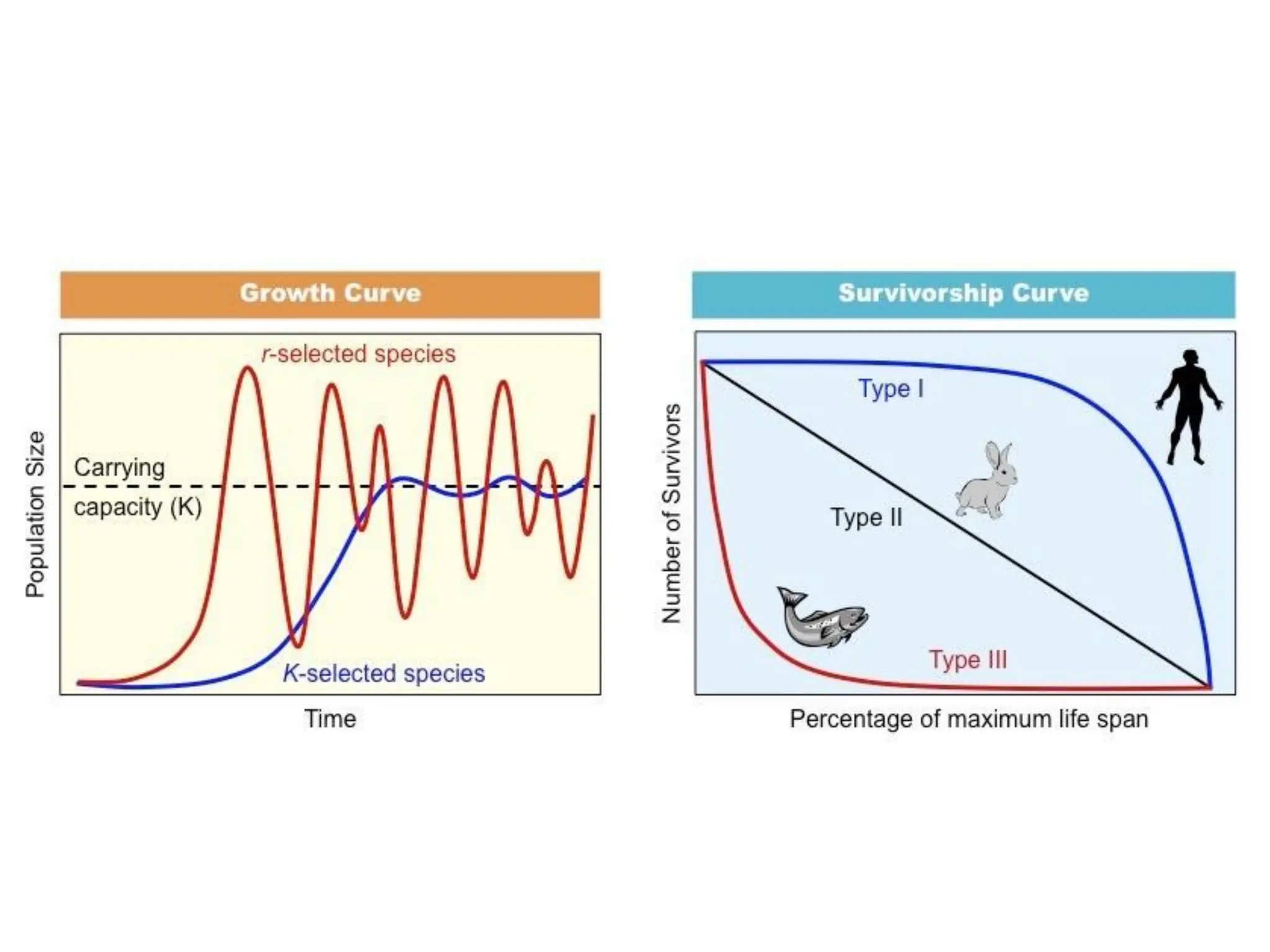
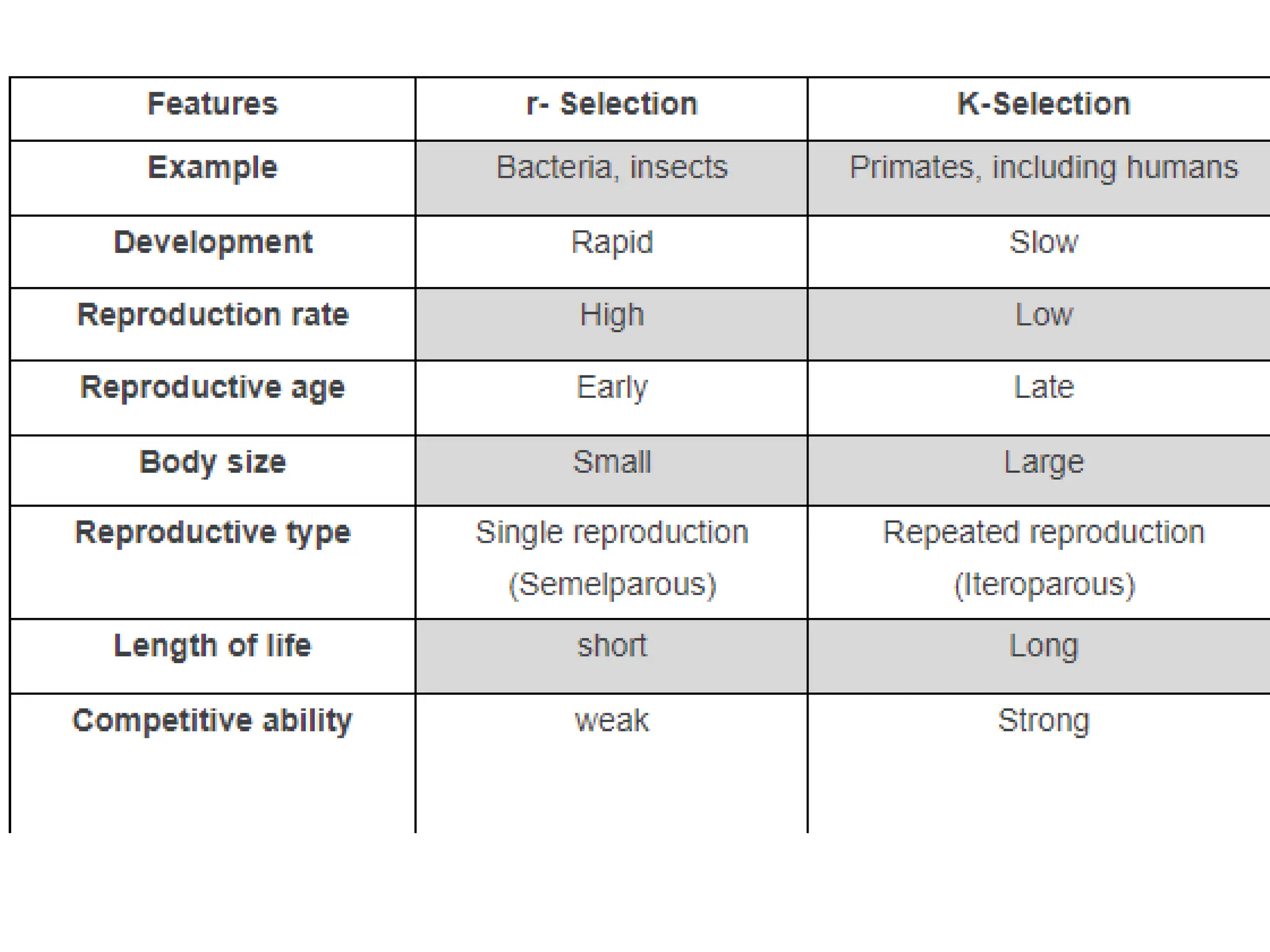
This document discusses r-selection and K-selection, which are concepts in ecology that classify species based on their life history traits and habitat stability. R-selected species are adapted to unstable, unpredictable environments by having high reproductive rates, rapid development, small body size, and producing many offspring with low survival rates. They exploit temporary habitats and respond quickly to disturbances. K-selected species are adapted to stable environments and compete for resources. They have slower growth, delayed reproduction, low reproductive output, and provide parental care. Their populations are near the carrying capacity of their environment and are limited by resources. The terms r and K relate to parameters in the logistic model of population growth.