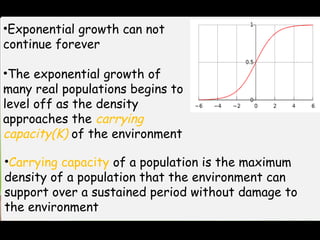
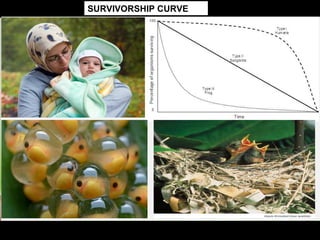
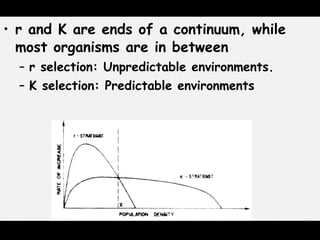
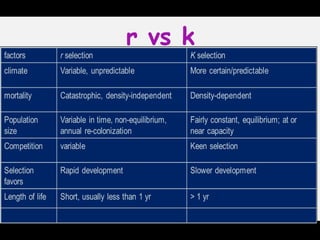
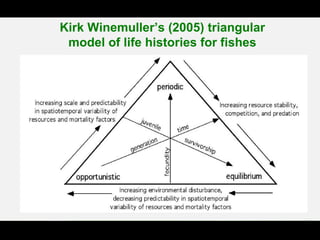
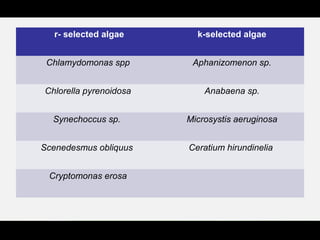
This document discusses r and K selection theory, which seeks to explain how traits evolve in response to environmental variation and mortality. It examines how traits are interrelated and constrained by ecology. R and K selection theory predicts demographic responses to disturbances at different spatial and temporal scales. The most notable example is MacArthur and Wilson's theory of r and K selection based on island biogeography. R-selected species thrive in variable environments and have high fecundity, while K-selected species exist in stable environments and invest more in parental care and fewer offspring. The r and K classification represents ends of a continuum, with most species falling somewhere in between.