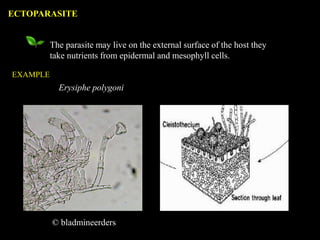
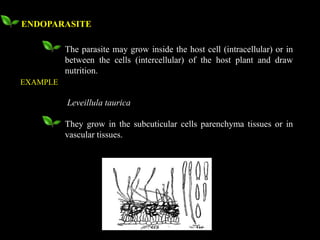
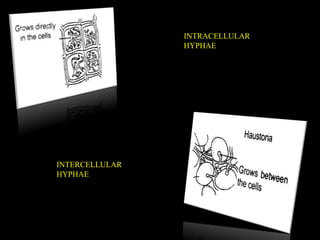
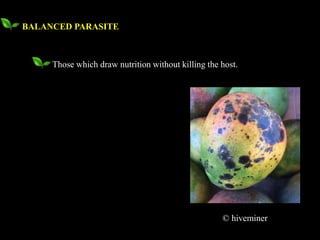
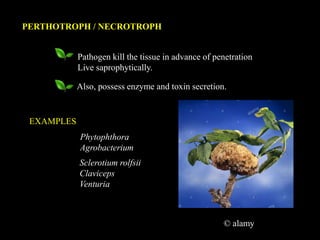
This document defines and describes different types of parasitism. It begins by defining a parasite as an organism that lives on or in another organism and obtains food for growth and reproduction. The main types discussed are ectoparasites, which live on the external surface of the host, and endoparasites, which live inside host cells or tissues. Other types include destructive parasites, which kill their host, and balanced parasites, which obtain nutrients without killing the host. Facultative parasites are normally saprophytic but can parasitize under conditions. Broad categories of parasitism include biotrophs, hemi-biotrophs, and necrotrophs/perthotrophs, which kill host