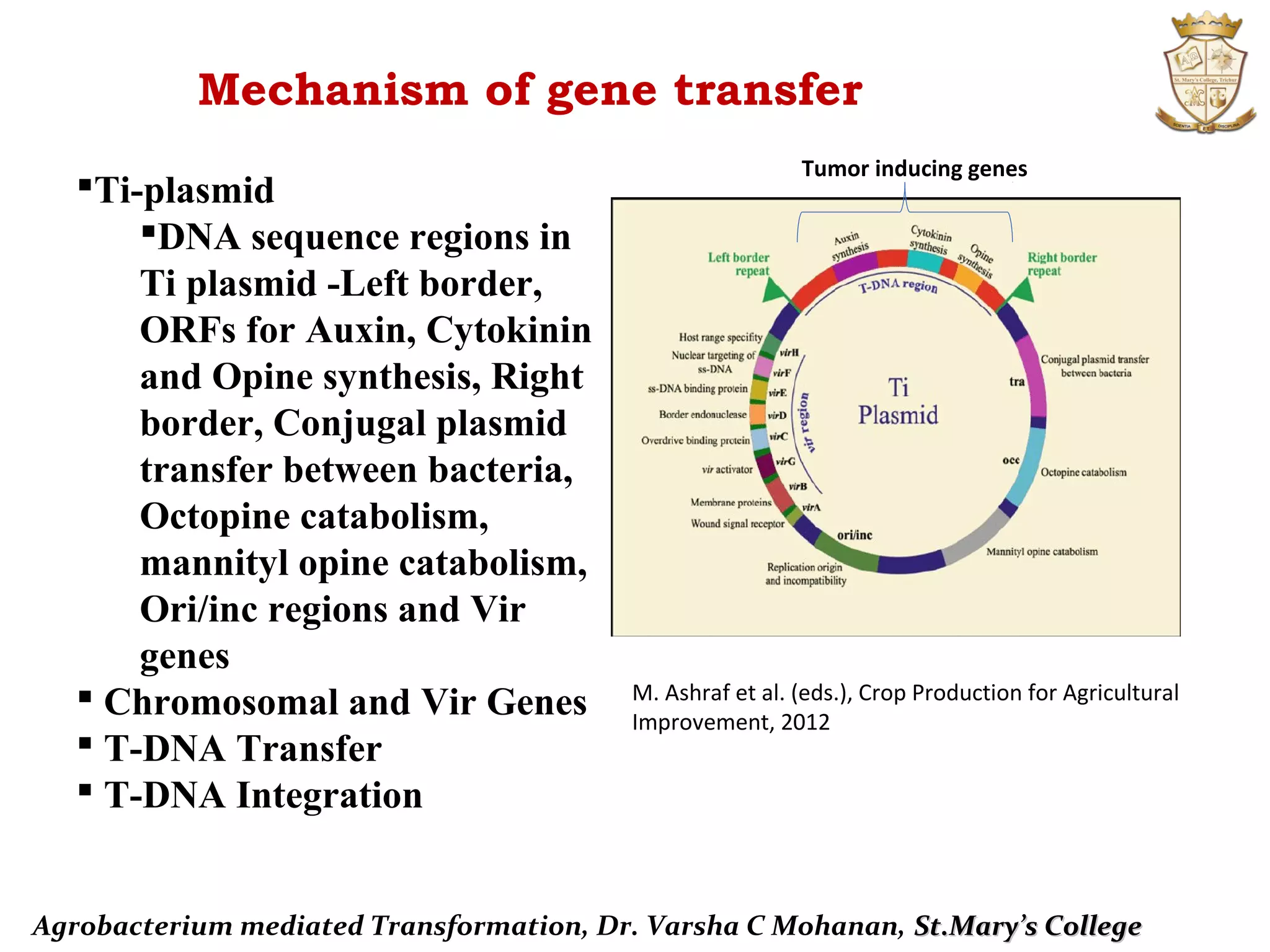
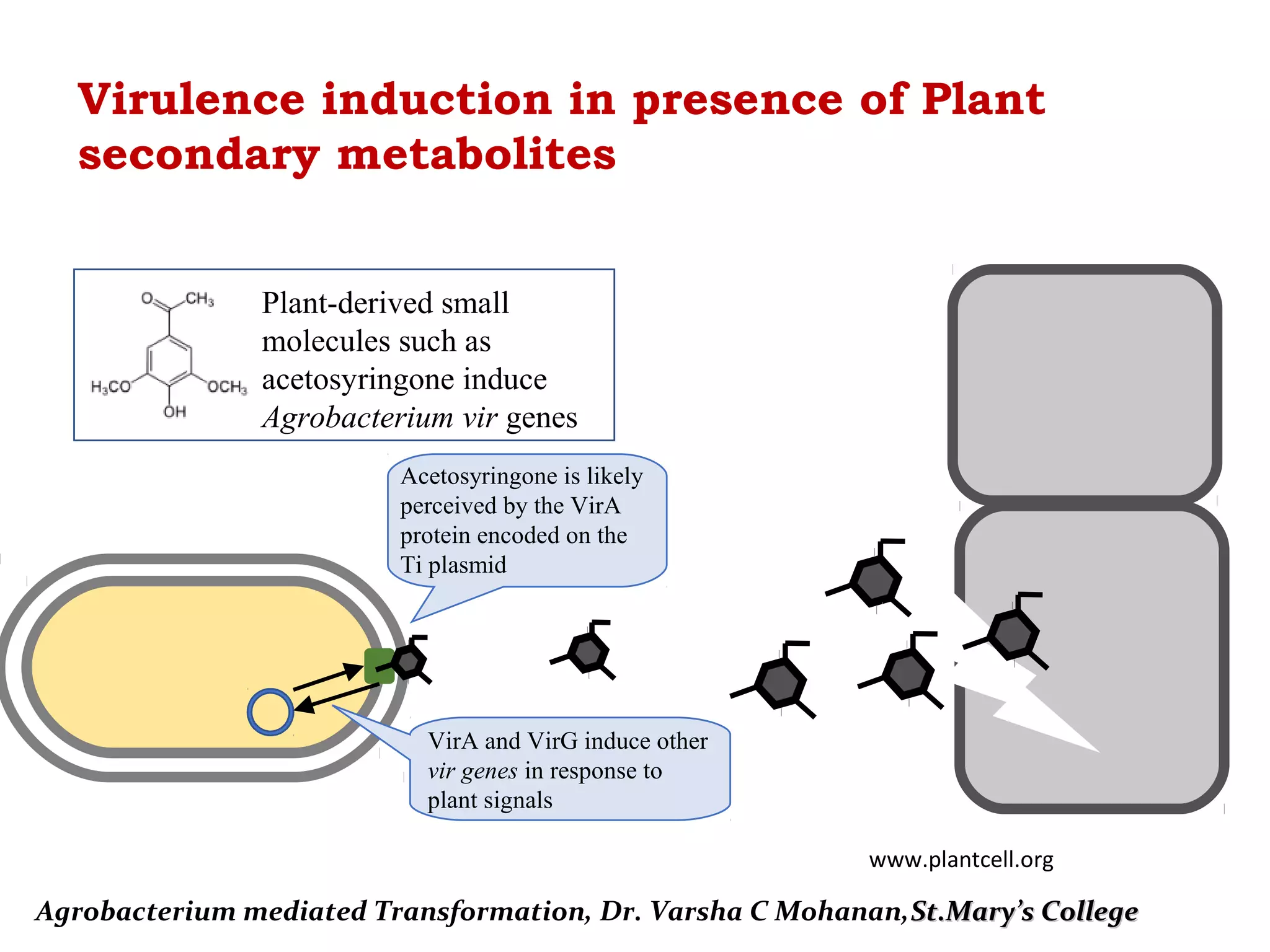
El documento detalla la transformación mediada por Agrobacterium, destacando su uso en la modificación genética de plantas. Explica el mecanismo de transferencia de ADN T desde Agrobacterium tumefaciens hacia las células vegetales, incluyendo la estructura del plásmido Ti y el sistema de vectores binarios. Se discuten también varios métodos de transformación para generar plantas genéticamente modificadas.