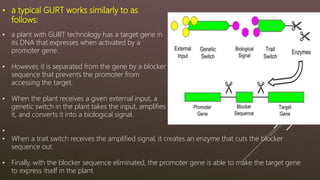
This document summarizes terminator gene technology, which genetically modifies plants to produce sterile seeds. It was developed by the seed industry to prevent seed saving. There are two types: varietal GURT (V-GURT) renders all subsequent seeds sterile, while trait GURT (T-GURT) switches traits on/off using chemical treatments. While it provides benefits to industry, it is controversial due to concerns over loss of biodiversity and impact on small farmers who rely on seed saving. Most countries have imposed a moratorium on field testing and commercialization of terminator seeds.