1) Biomechanics refers to the study of engineering and physics principles applied to living systems, especially the human body. It involves understanding forces and mechanics in anatomy.
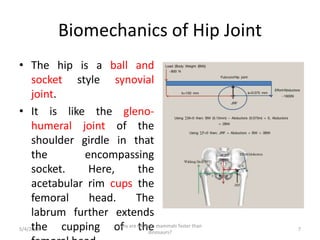
2) The hip is a ball and socket joint like the shoulder, but more stable due to forces experienced. It allows flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
3) Understanding hip biomechanics requires knowledge of lower body mechanics and gait, along with the functions of surrounding muscles and ligaments like the iliotibial tract. Accurately determining the hip joint center is important for gait analysis.