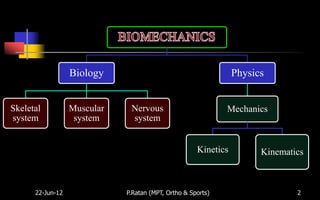
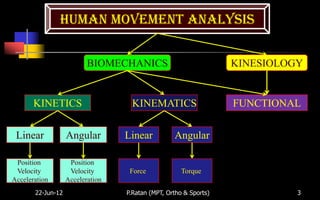
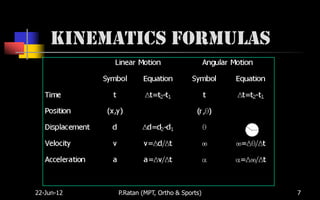
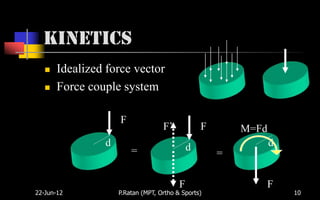
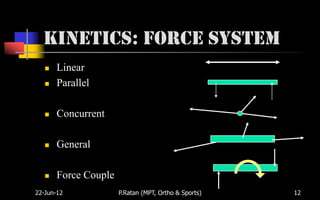
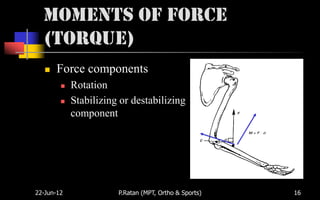
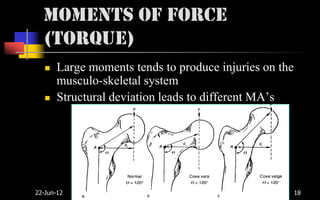
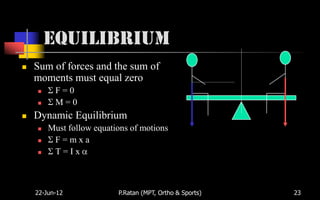
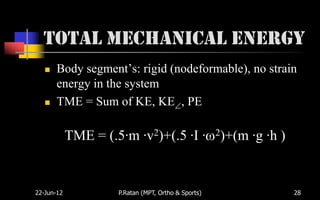
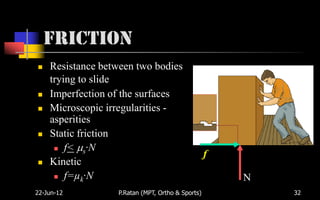
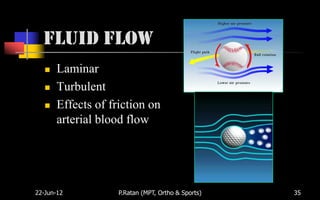
Biomechanics is the study of biological systems using mechanical principles. It draws from biology and physics to describe the movement of living organisms. Biomechanics aids in understanding human movement through analyzing kinetics, which examines causes of motion like forces and torques, and kinematics, which describes motion in terms of displacement, velocity and acceleration. Proper biomechanical analysis is important for understanding injuries and designing rehabilitation.