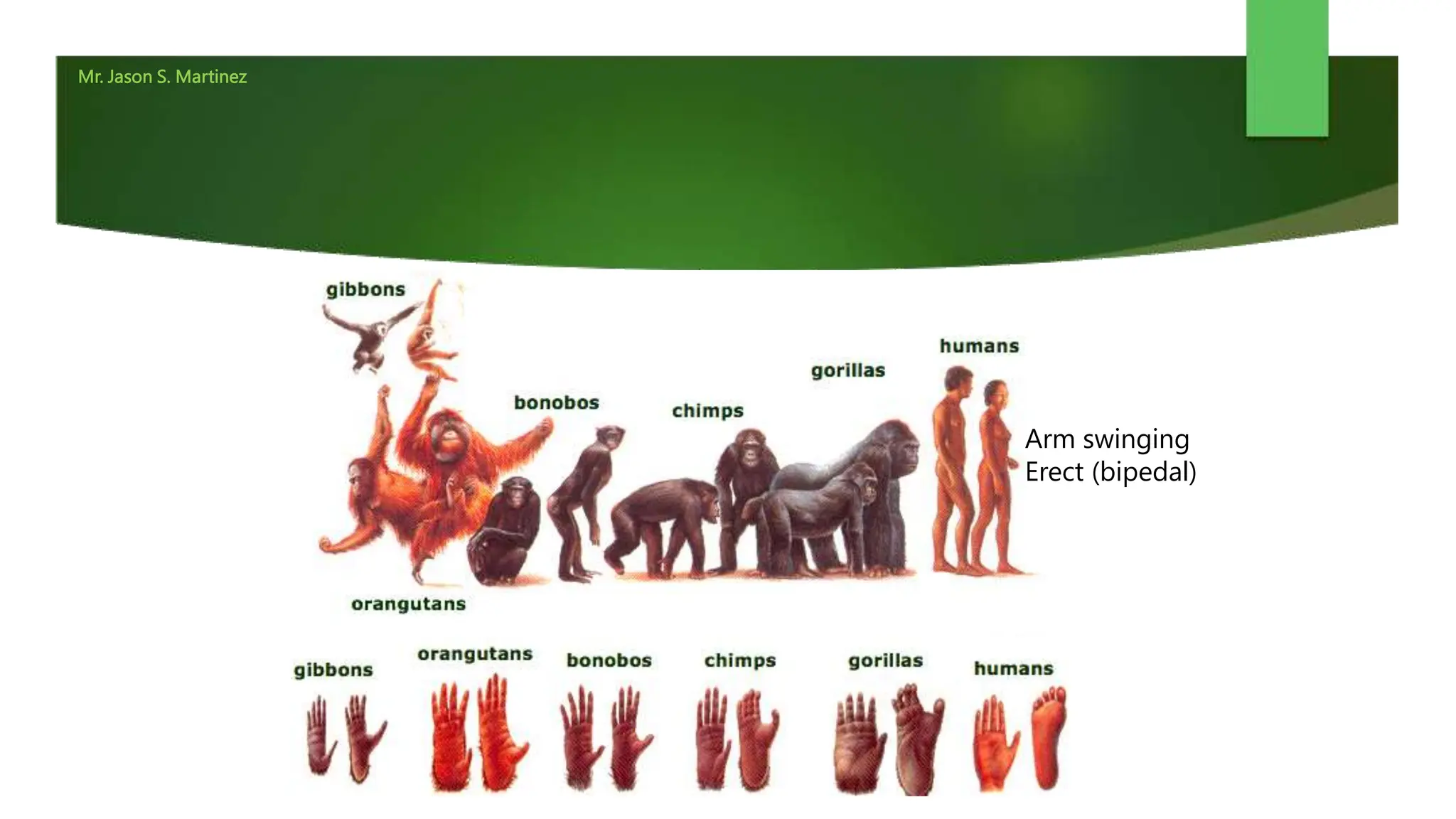
The document discusses the biomechanics of animal movement. It defines key terms like myofibril, sarcomere, and joints. It describes how muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones work together through lever systems to create movement. Specific types of locomotion are examined, like bipedal walking in humans, which requires fluid alternation between stance and swing phases. The advantages of locomotion for organisms are finding food, shelter, reproduction and escaping predators.