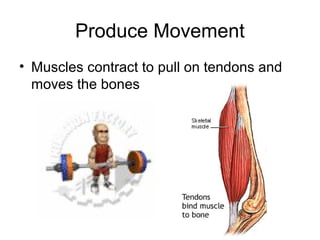
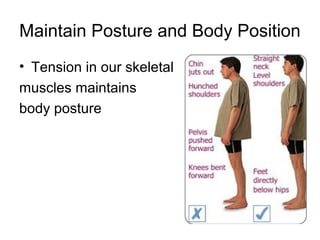
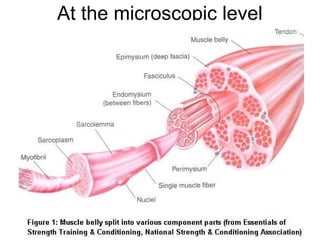
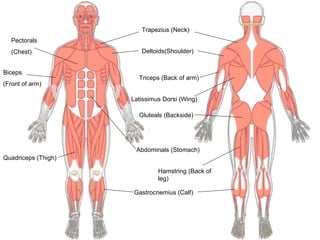
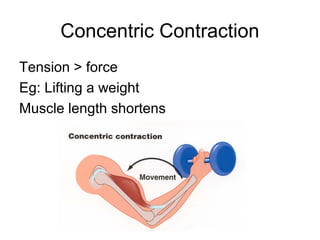
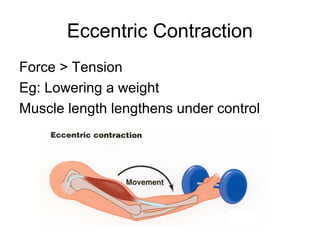
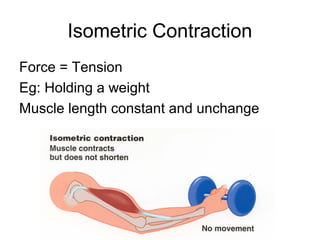
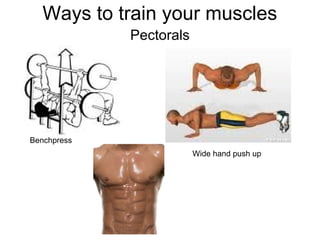
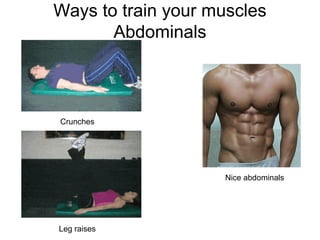
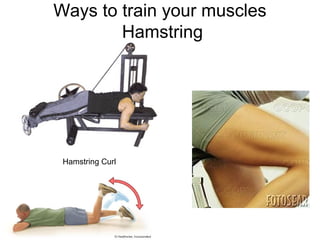
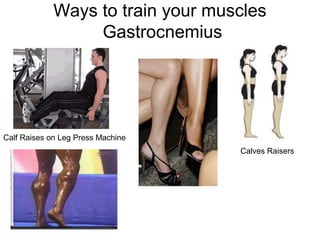
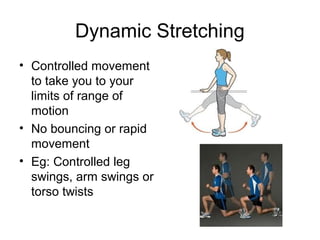
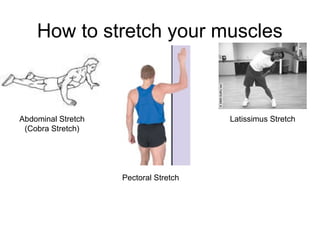
This document provides information about the skeletal muscle system. It discusses the characteristics of muscle tissue including excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity. It also describes the functions of skeletal muscles in producing movement, maintaining posture and temperature. Different muscle fiber types, muscle names, and contraction modes are outlined. The benefits of strength training and ways to train specific muscles through exercises are explained. Finally, the importance of stretching and different stretching techniques are covered.