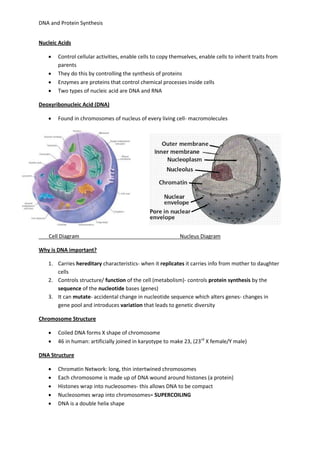
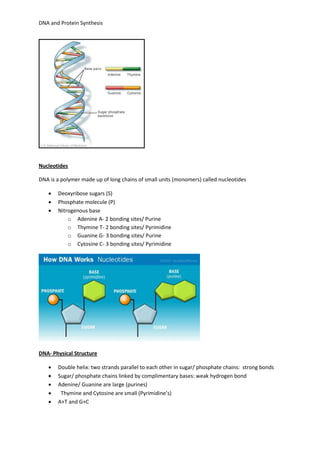
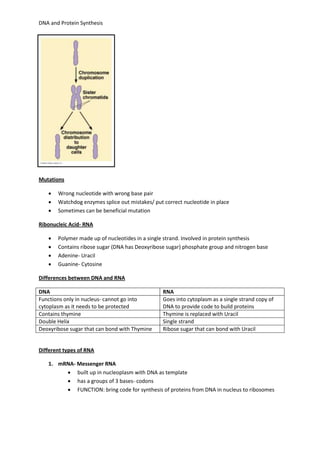
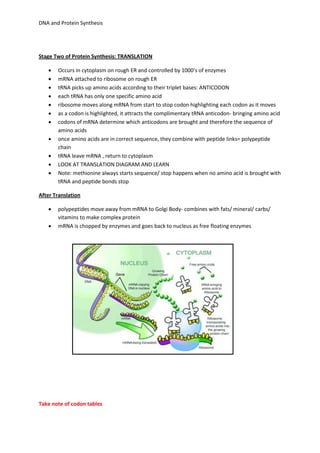
DNA controls cellular activities and protein synthesis. It is found in the cell nucleus as a double-stranded helix made up of nucleotides. DNA replicates itself using DNA polymerase and stores the genetic code in genes that determine protein sequences. During transcription, a complementary mRNA strand is produced from DNA in the nucleus. Translation then occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where tRNA brings amino acids to the ribosome according to mRNA codons, assembling proteins from the genetic code carried by DNA.