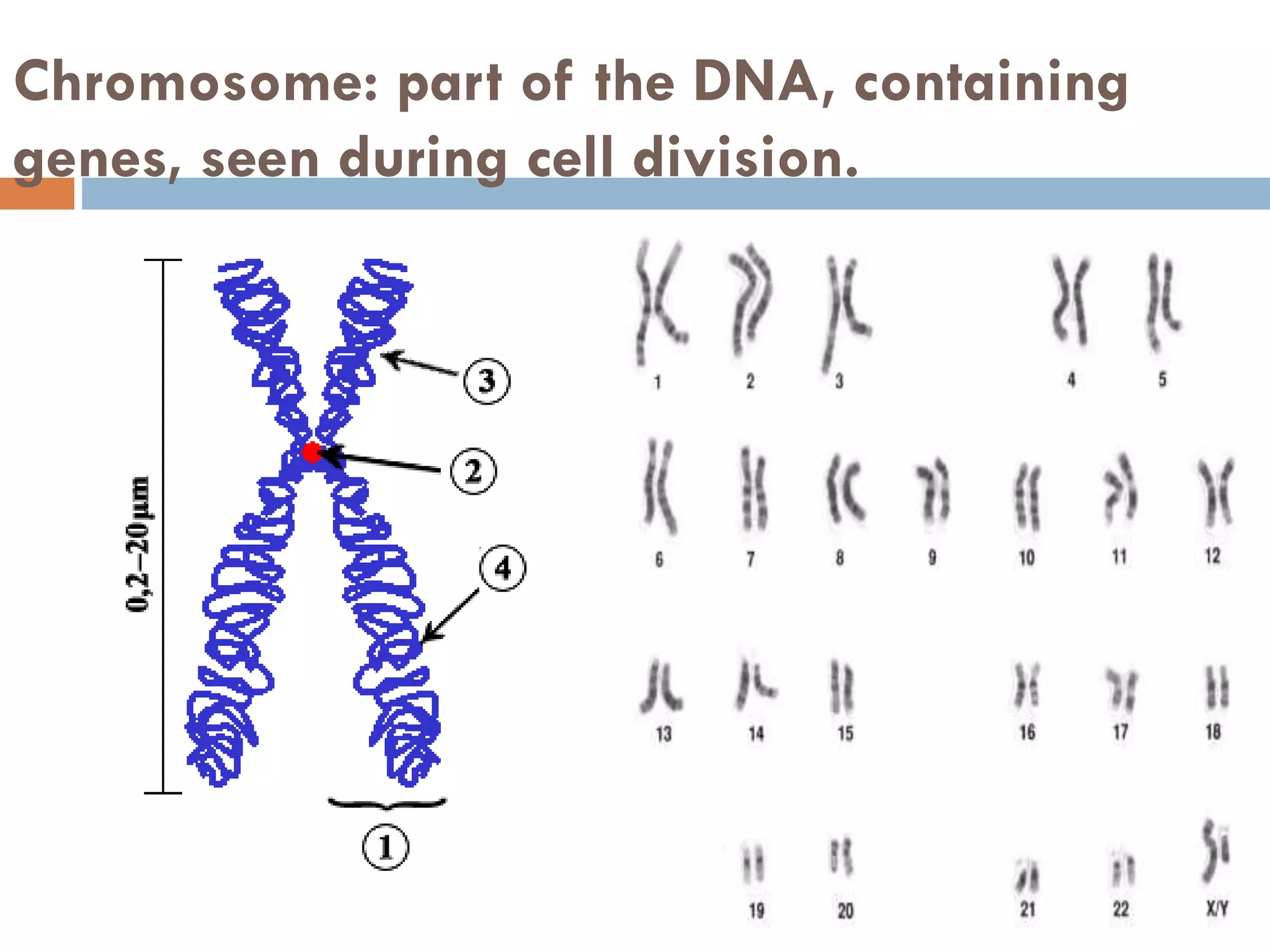
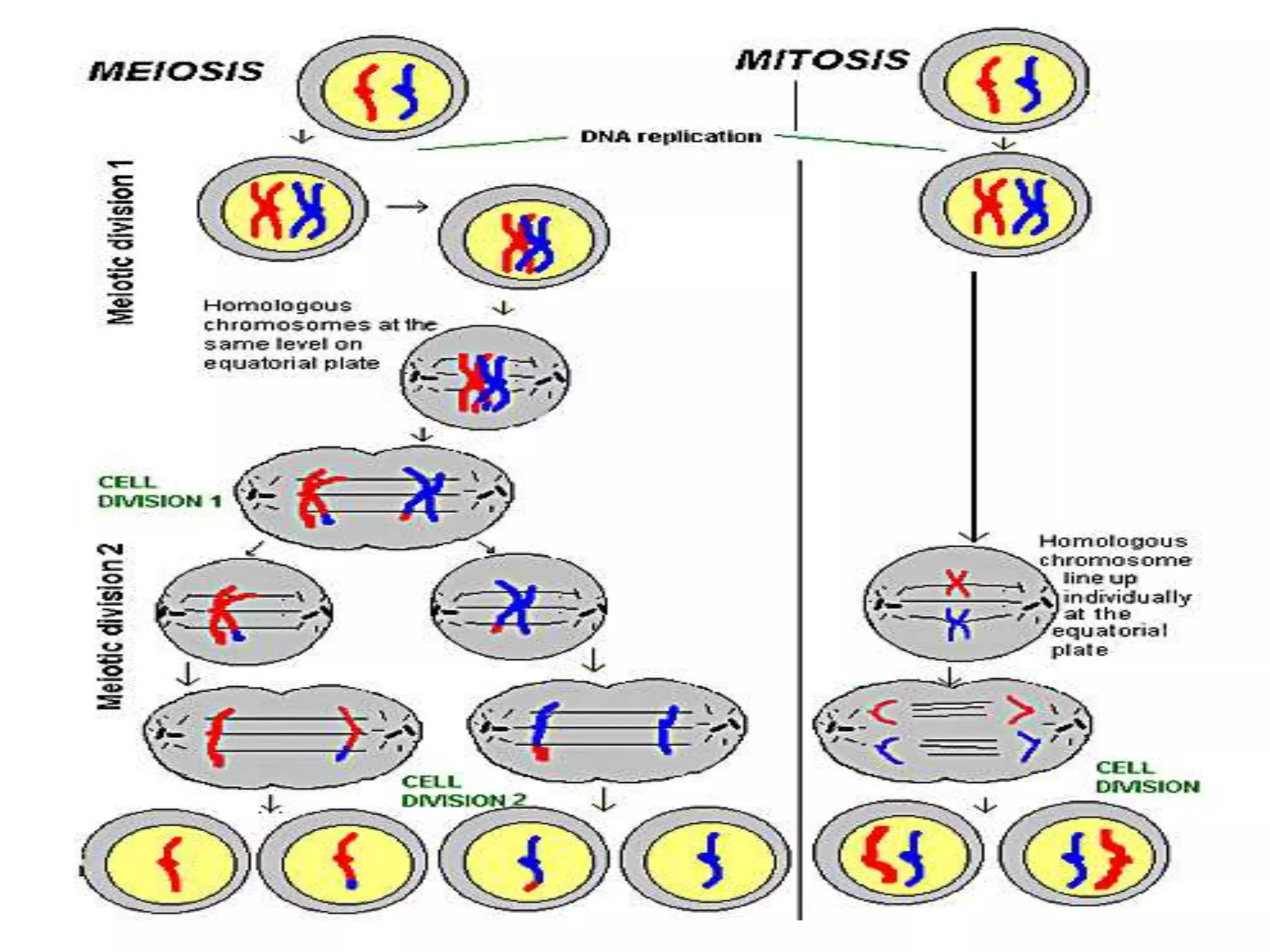
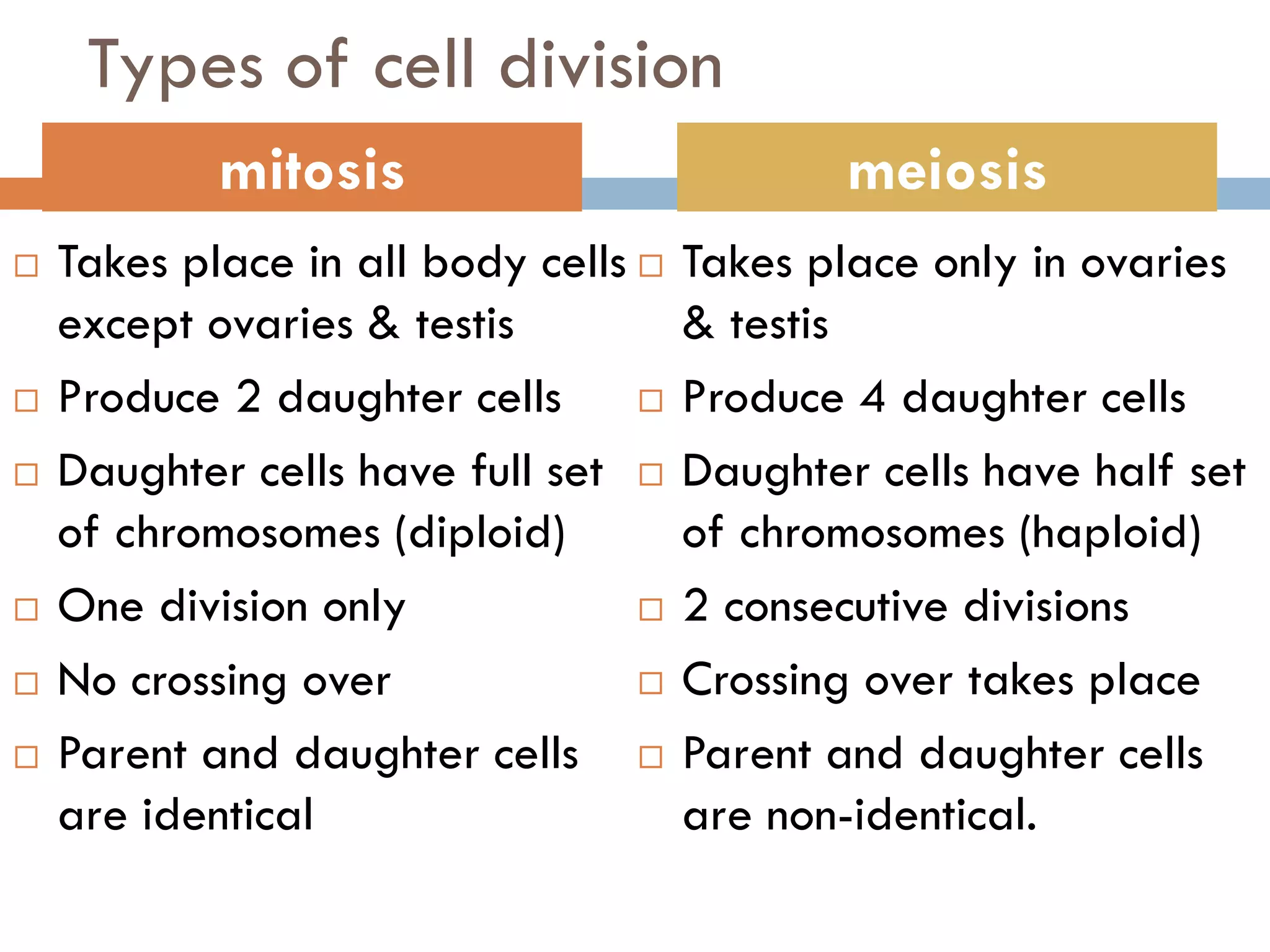
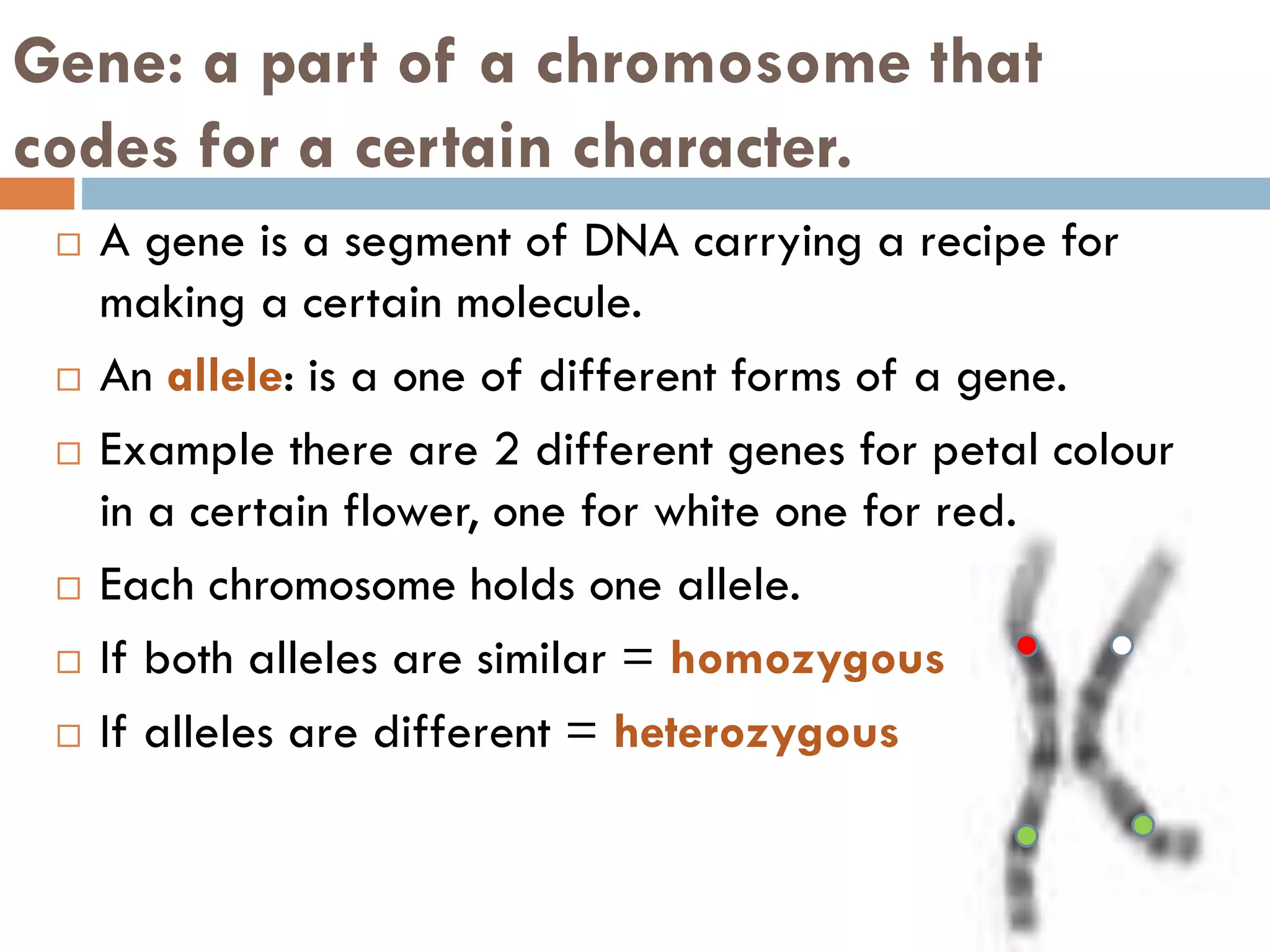
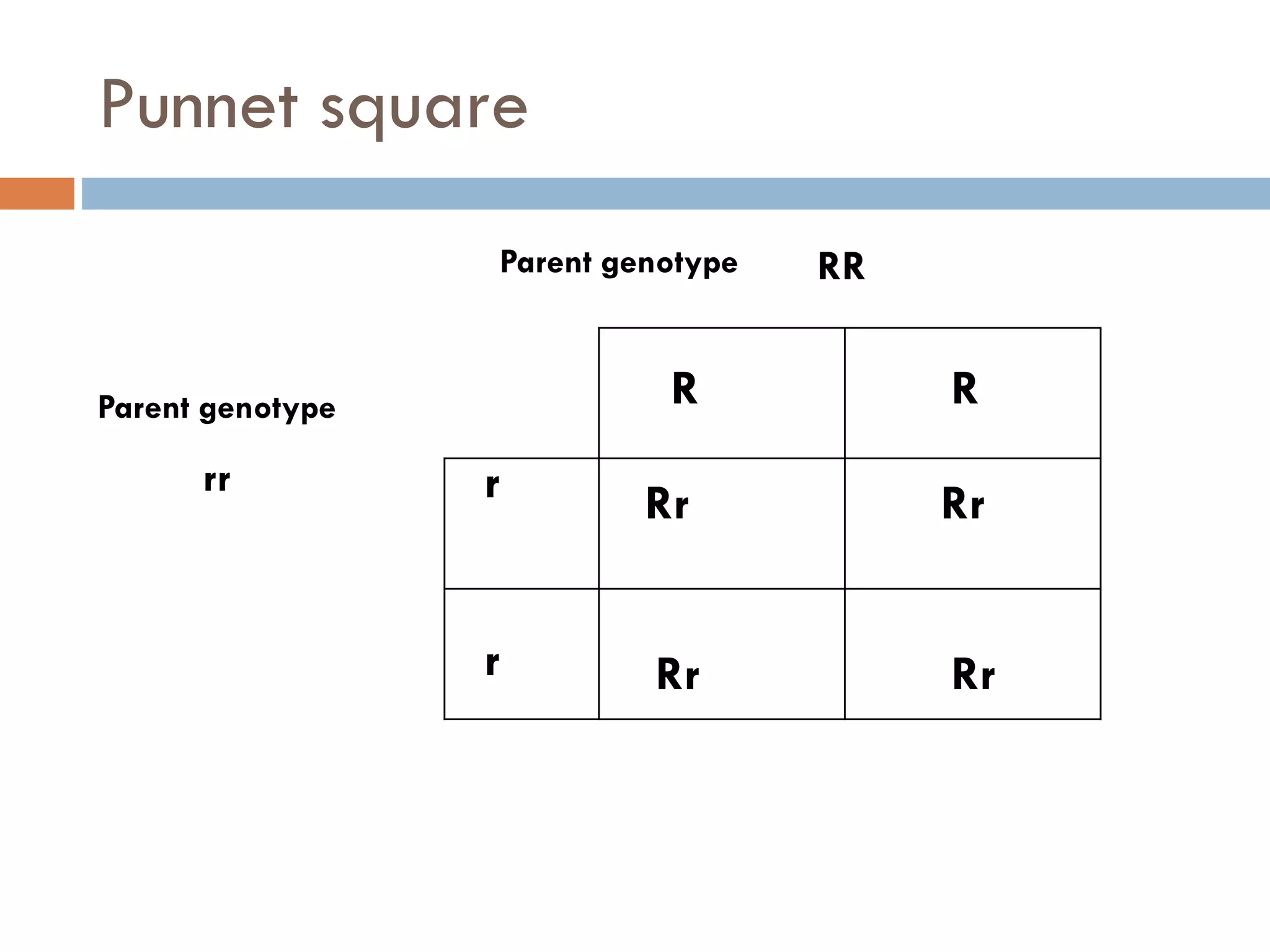
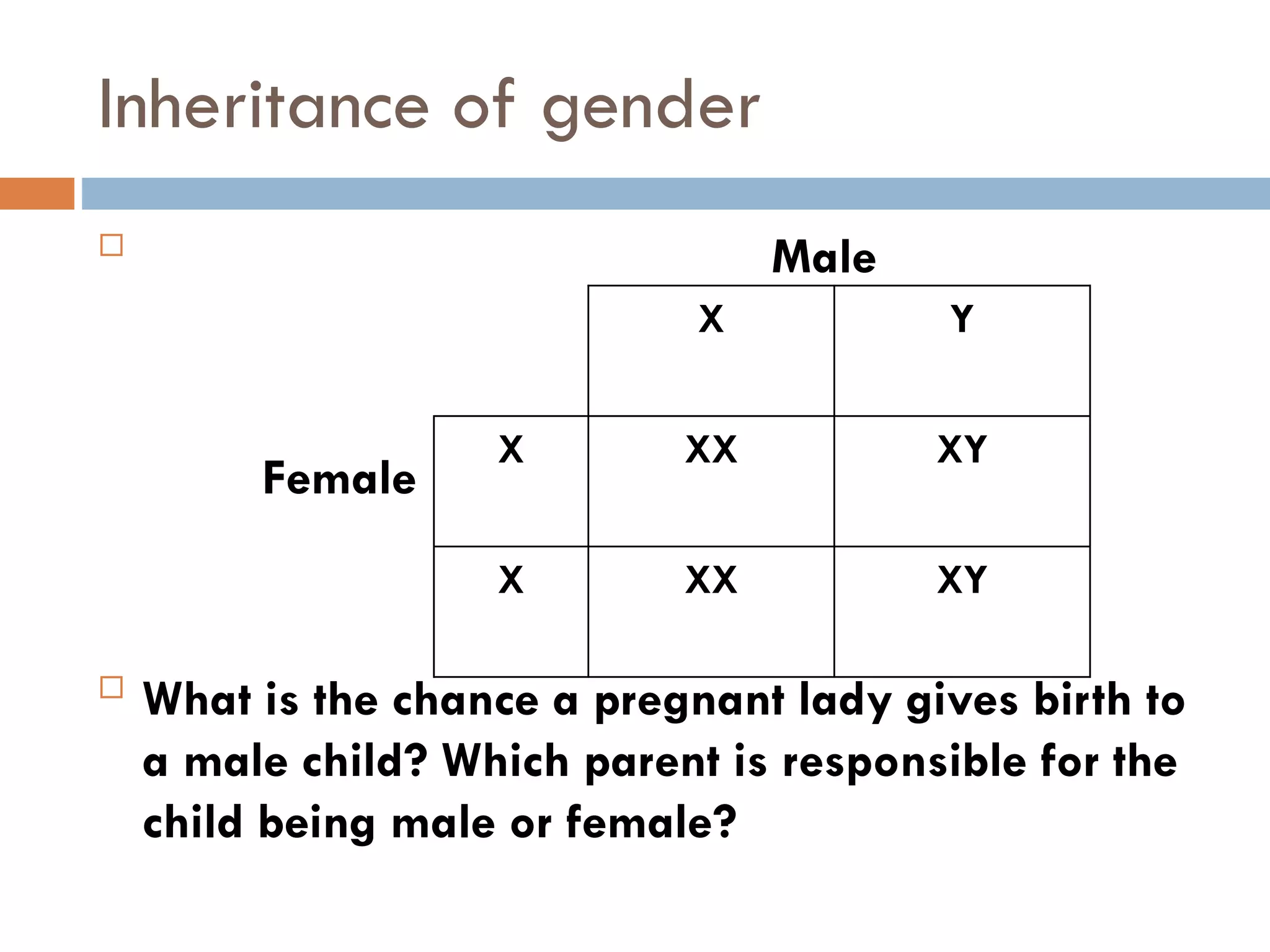
Cell division and inheritance allows organisms to grow and pass genetic information between generations. During cell division, DNA is replicated and divided between new cells so they have the same characteristics. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis produces identical cells while meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. Genes determine traits and alleles are different forms of genes. Dominant alleles show up in offspring while recessive alleles only show if an organism is homozygous recessive. Genetic crosses using Punnett squares can predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes from parent genotypes.