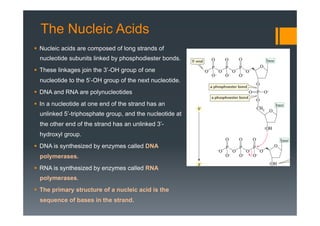
This document introduces bio-organic chemistry with a focus on the synthesis and structure of nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA. It explains the roles of nucleotides, transcription, and translation in protein synthesis, as well as the biosynthesis of cholesterol and alkaloids. Additionally, it poses a series of questions related to the topics covered, aiming to deepen understanding of nucleic acids and their biological significance.









![Formation of
complementry base
pairs
• [adenine] = [thymine]
• [guanine] = [cytosine]
• Adenine (A) always paired with thymine (T)
• Guanine (G) always paired with cytosine (C)
• Base pairing in DNA: Adenine and thymine
form two hydrogen bonds;
• cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen
bonds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uniti-bioorganicchemistry-190218170513/85/Unit-i-bio-organic-chemistry-11-320.jpg)






















