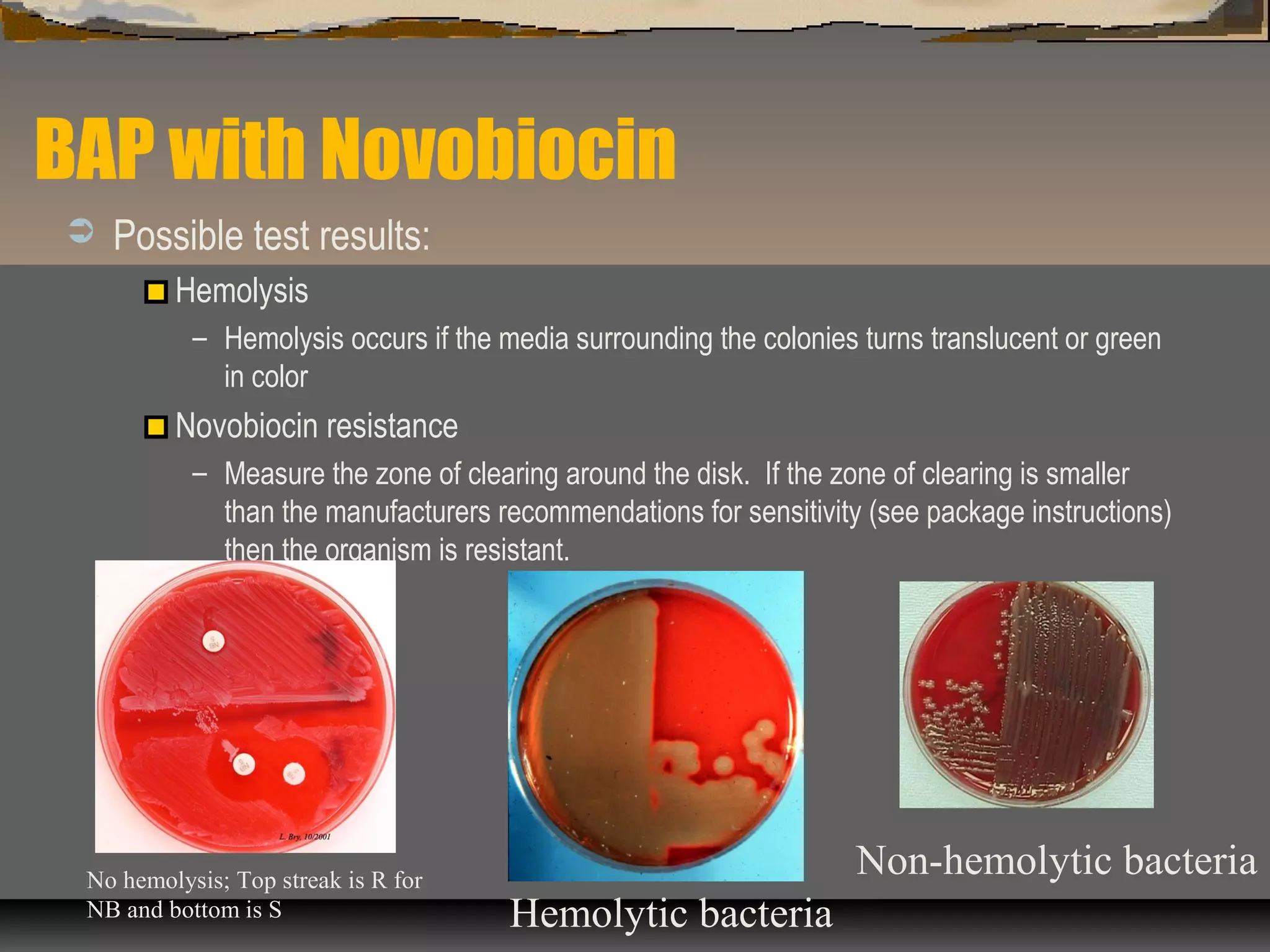
The document outlines various biochemical tests for identifying and differentiating species of the Enterobacteriaceae family and Staphylococcus. It includes detailed procedures, properties being tested, media and reagents, as well as methods for interpreting results for tests such as indole, methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, citrate, H2S production, urea hydrolysis, motility, lactose and sucrose fermentation, glucose fermentation, and coagulase. Each test aims to determine specific capabilities of bacteria, aiding in proper identification.