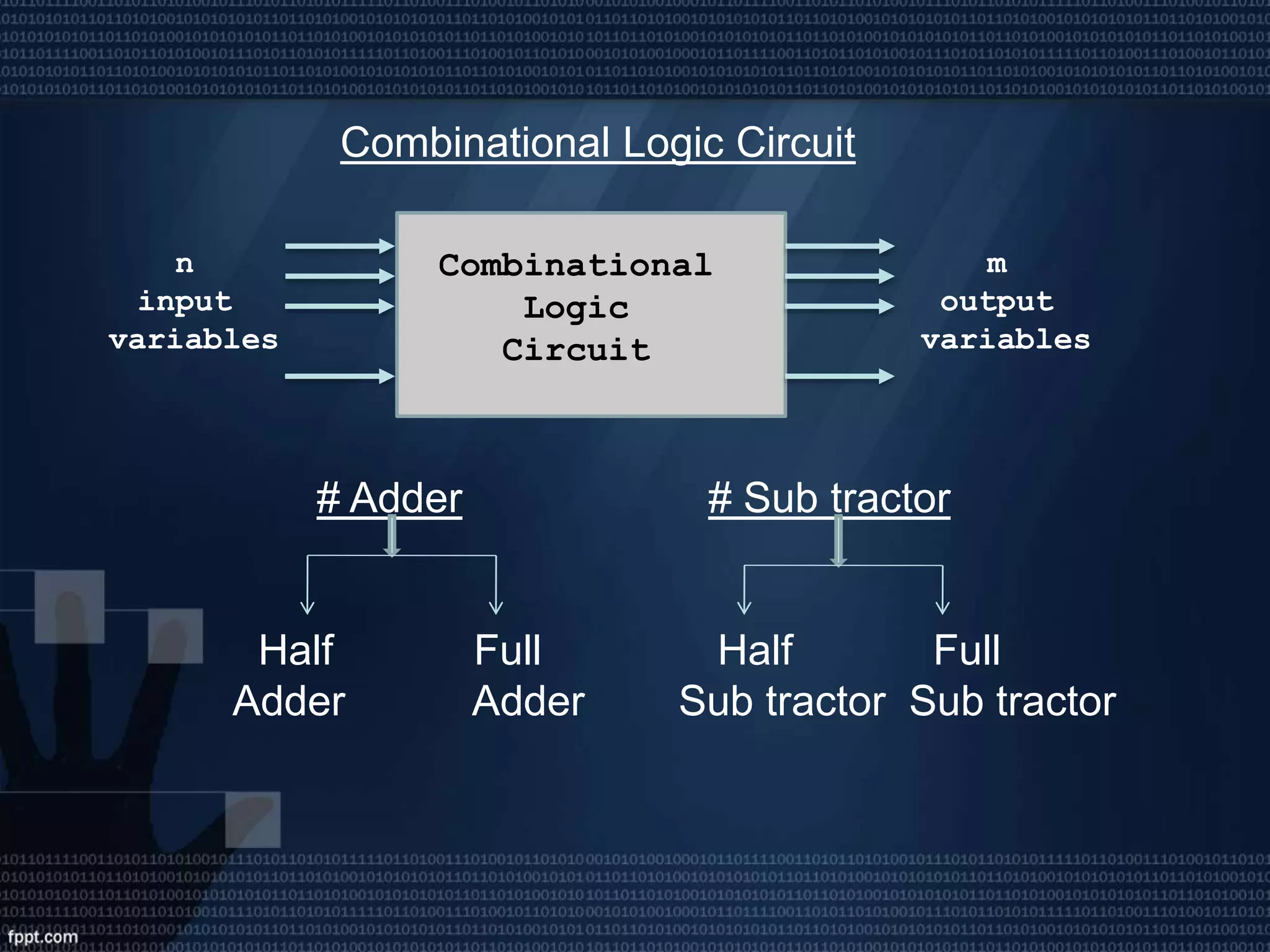
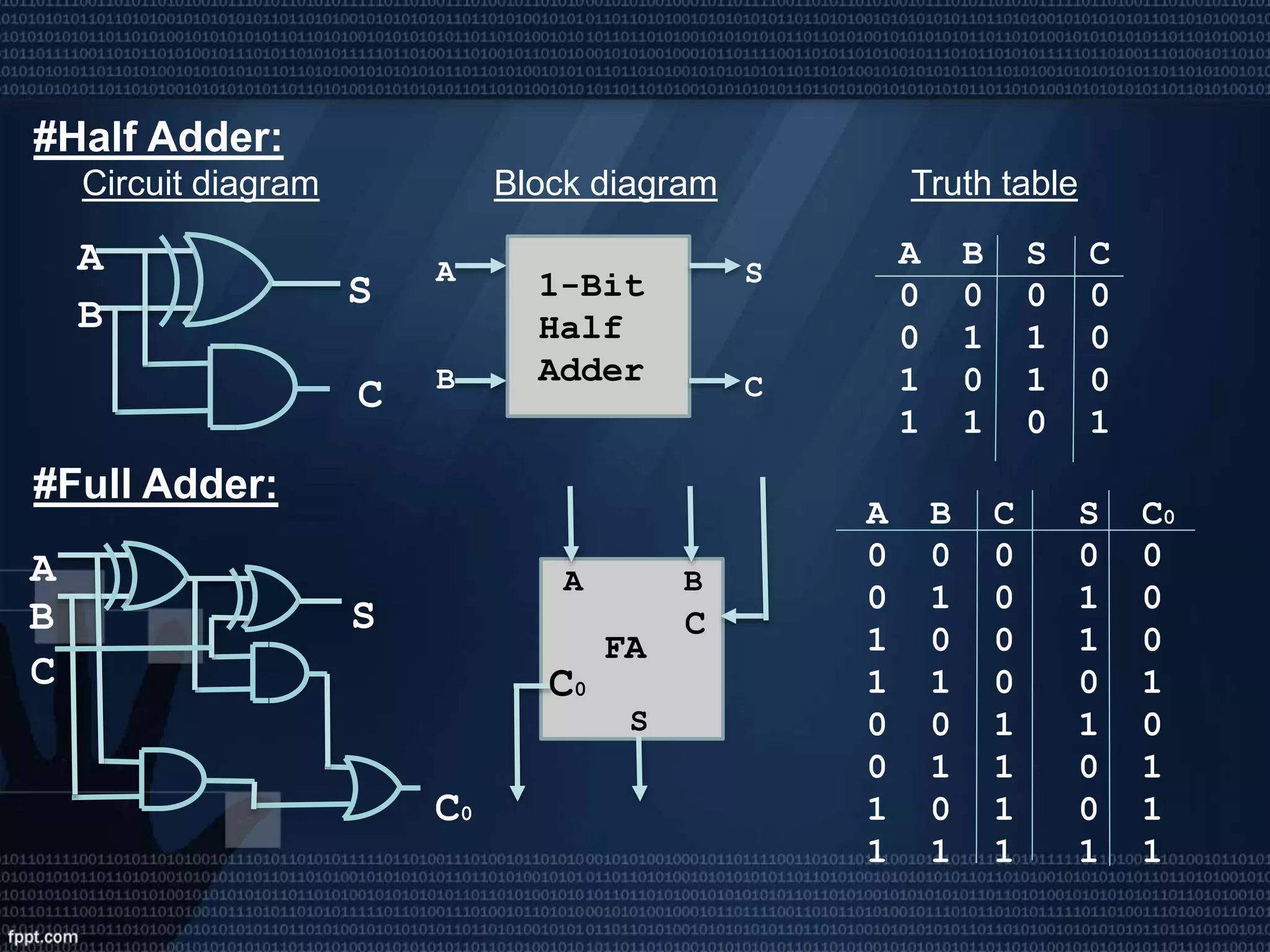
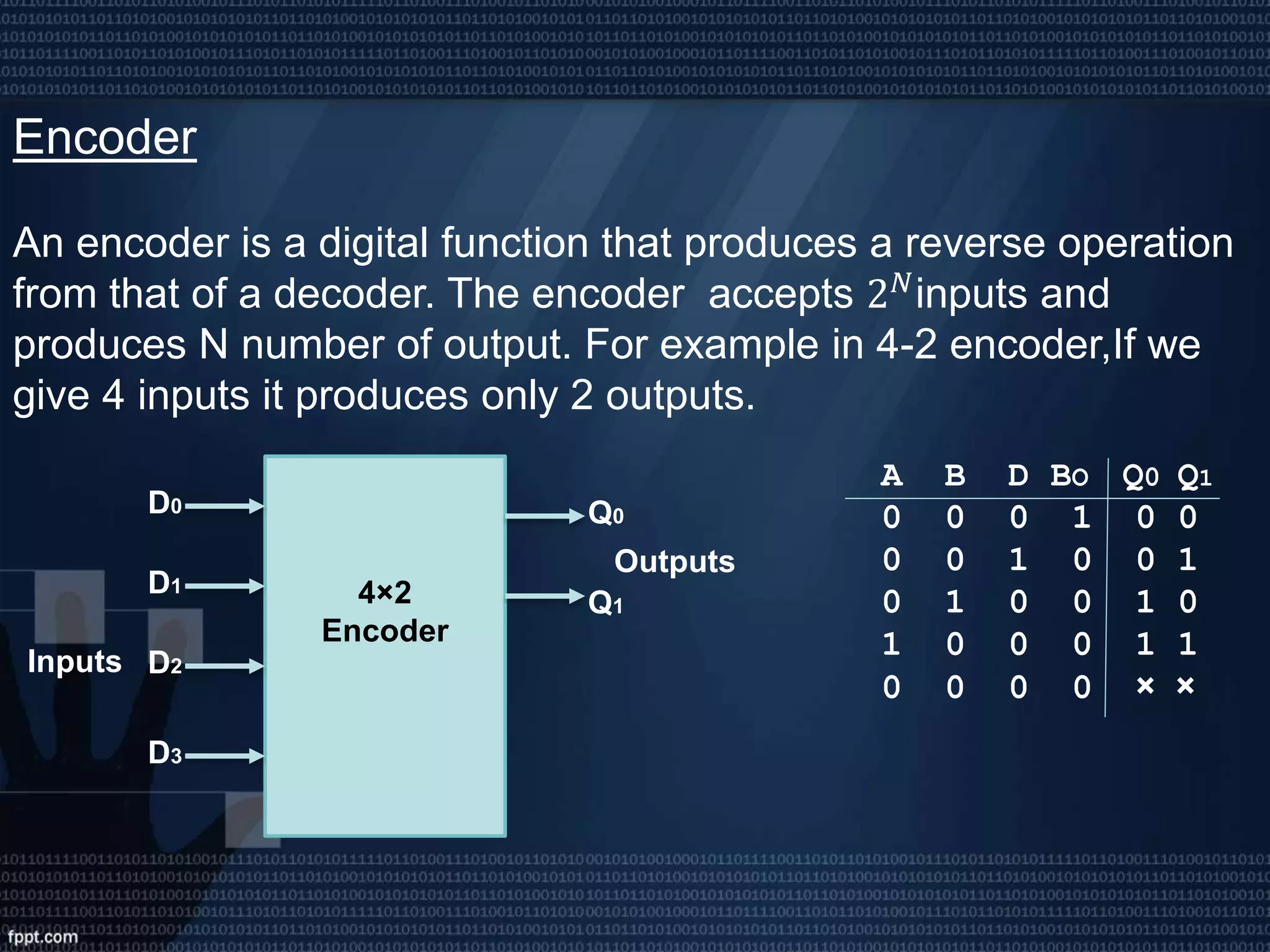
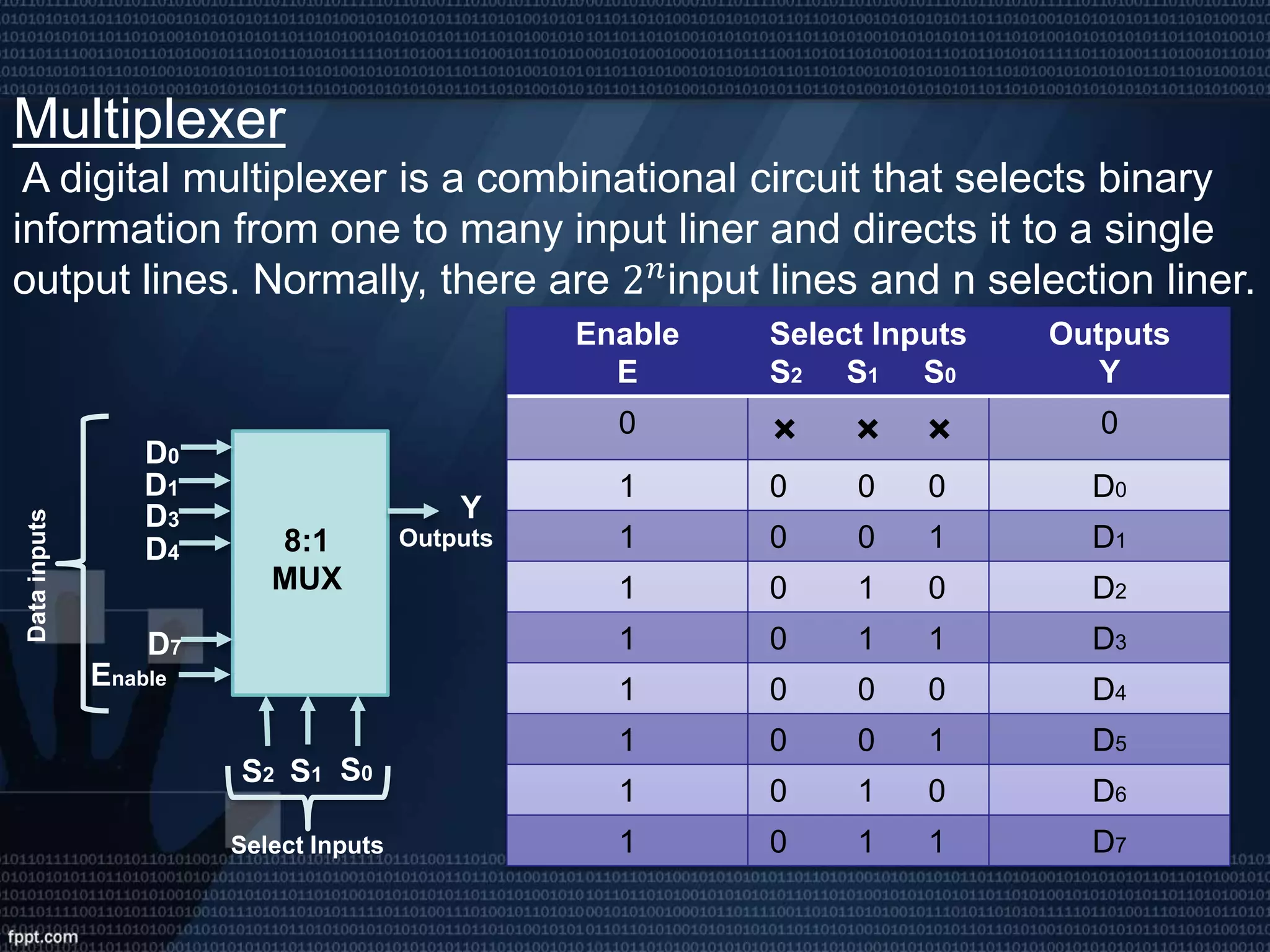
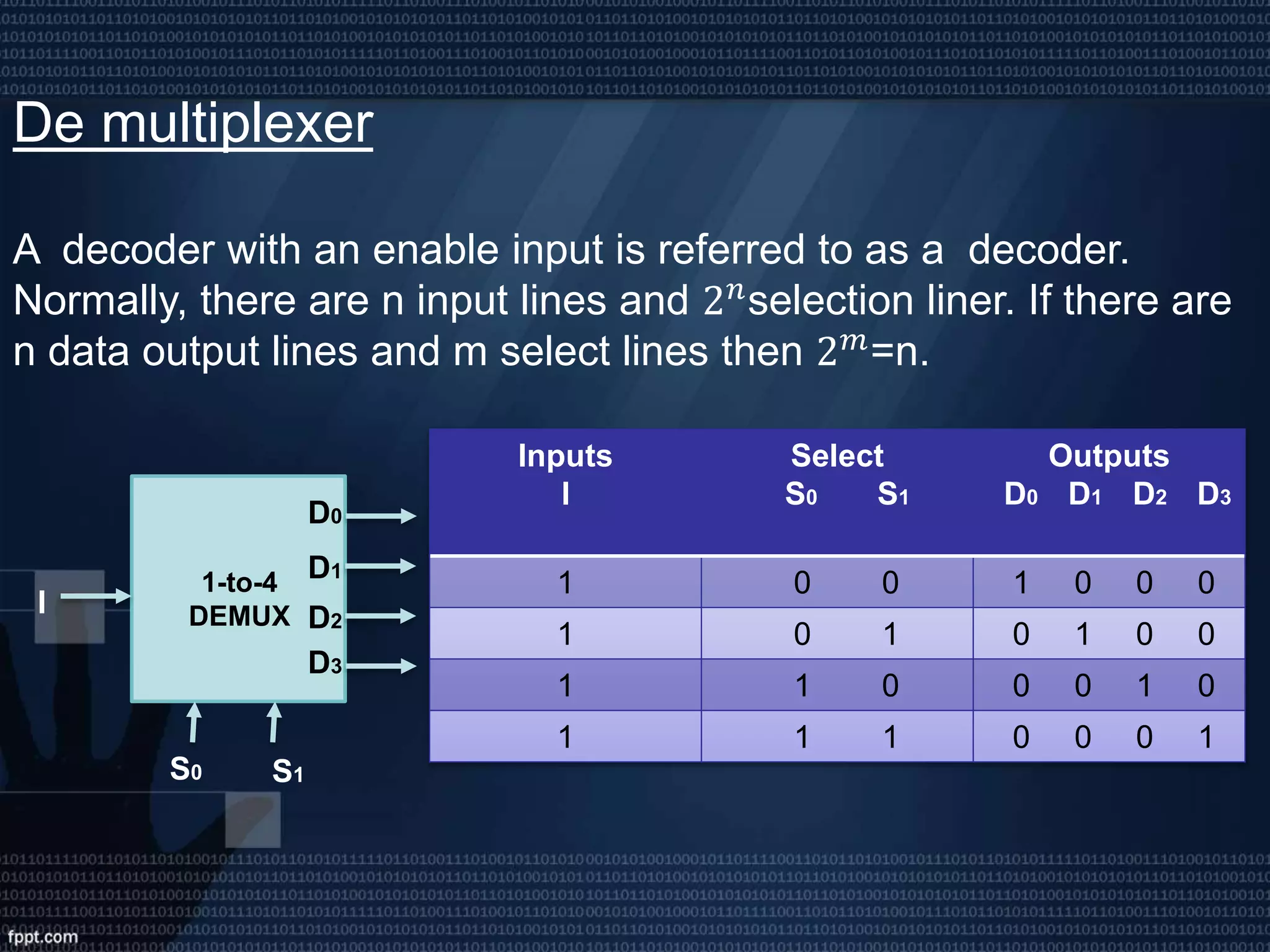
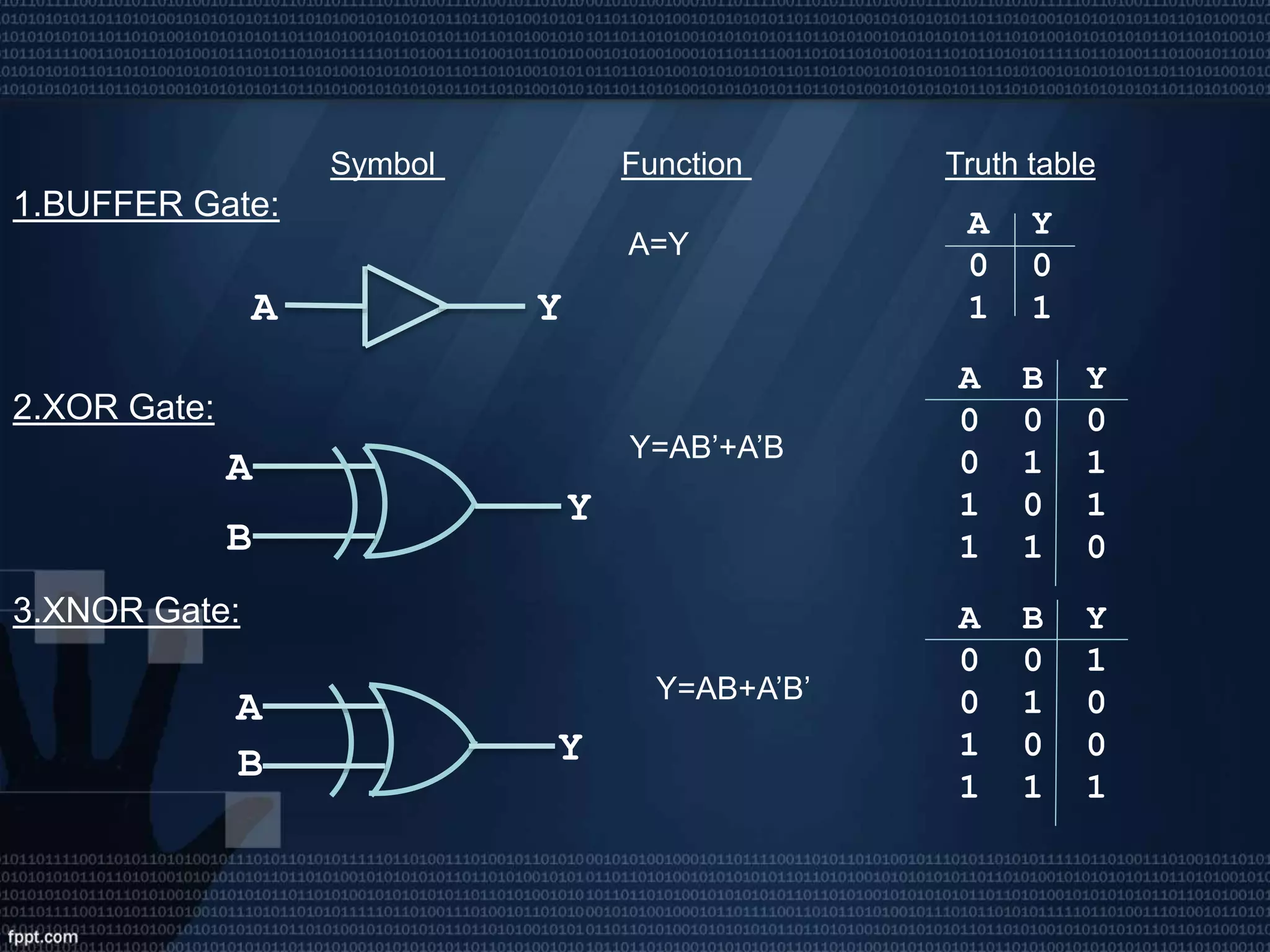
This presentation introduces digital logic circuits such as encoders, decoders, multiplexers, demultiplexers and logic gates. It is presented by a group consisting of 5 members whose names and student IDs are listed. The topics covered include the definitions of complements, combinational logic circuits, encoder and decoder functions, how multiplexers and demultiplexers work, and the truth tables of common logic gates.