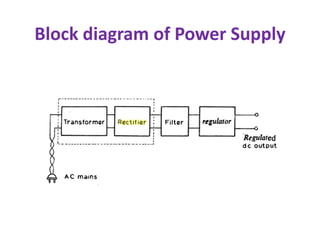
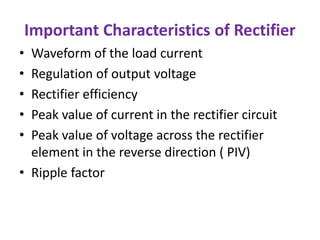
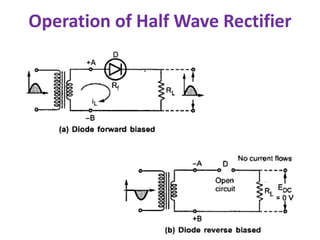
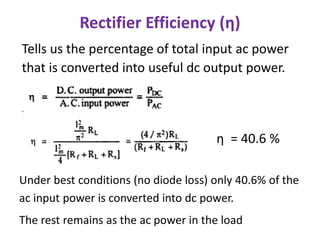
This document discusses different types of rectifiers used in power supplies to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). It describes half wave rectifiers, full wave rectifiers, center tap rectifiers, and bridge rectifiers. For each type, it covers the circuit diagram, operation, waveforms, efficiency, ripple factor, and applications. The full wave and bridge rectifiers are more efficient than the half wave rectifier at converting AC to DC with less ripple. Bridge rectifiers do not require a center tap transformer but have a higher voltage drop across the diodes. Rectifiers are used in applications like mobile chargers and laptop adapters to provide stable DC power from an AC source.