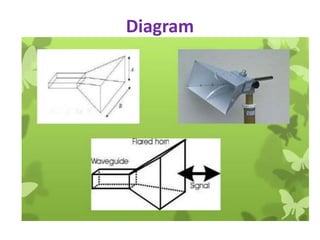
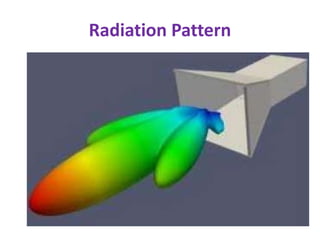
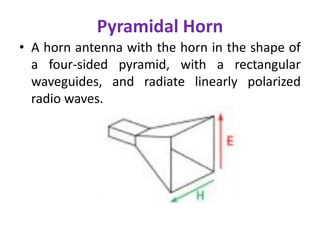
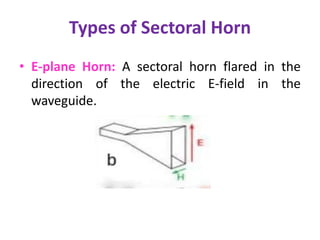
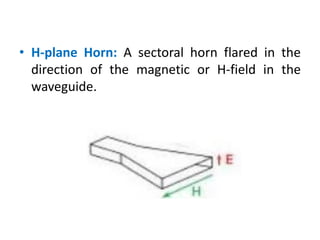
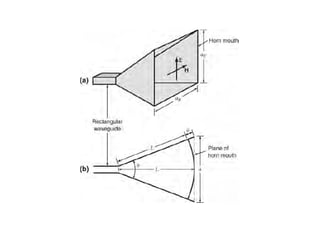
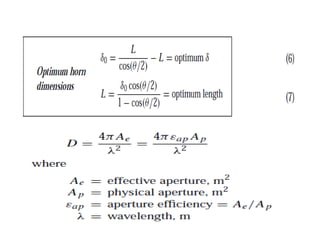
A horn antenna is a metal waveguide shaped like a flaring horn that directs radio waves in a beam. It serves as a transition between a waveguide and free space, allowing waves from the waveguide to radiate efficiently into space with minimal reflection. The wide aperture of the horn projects the waves in a narrow beam. Common types of horn antennas include pyramidal, sectoral, conical, and septum horns, which can have different flare angles and expansion curves to produce various beam profiles. A horn antenna works similarly to an acoustic horn, providing impedance matching to efficiently transmit waves from the confined waveguide into open space.