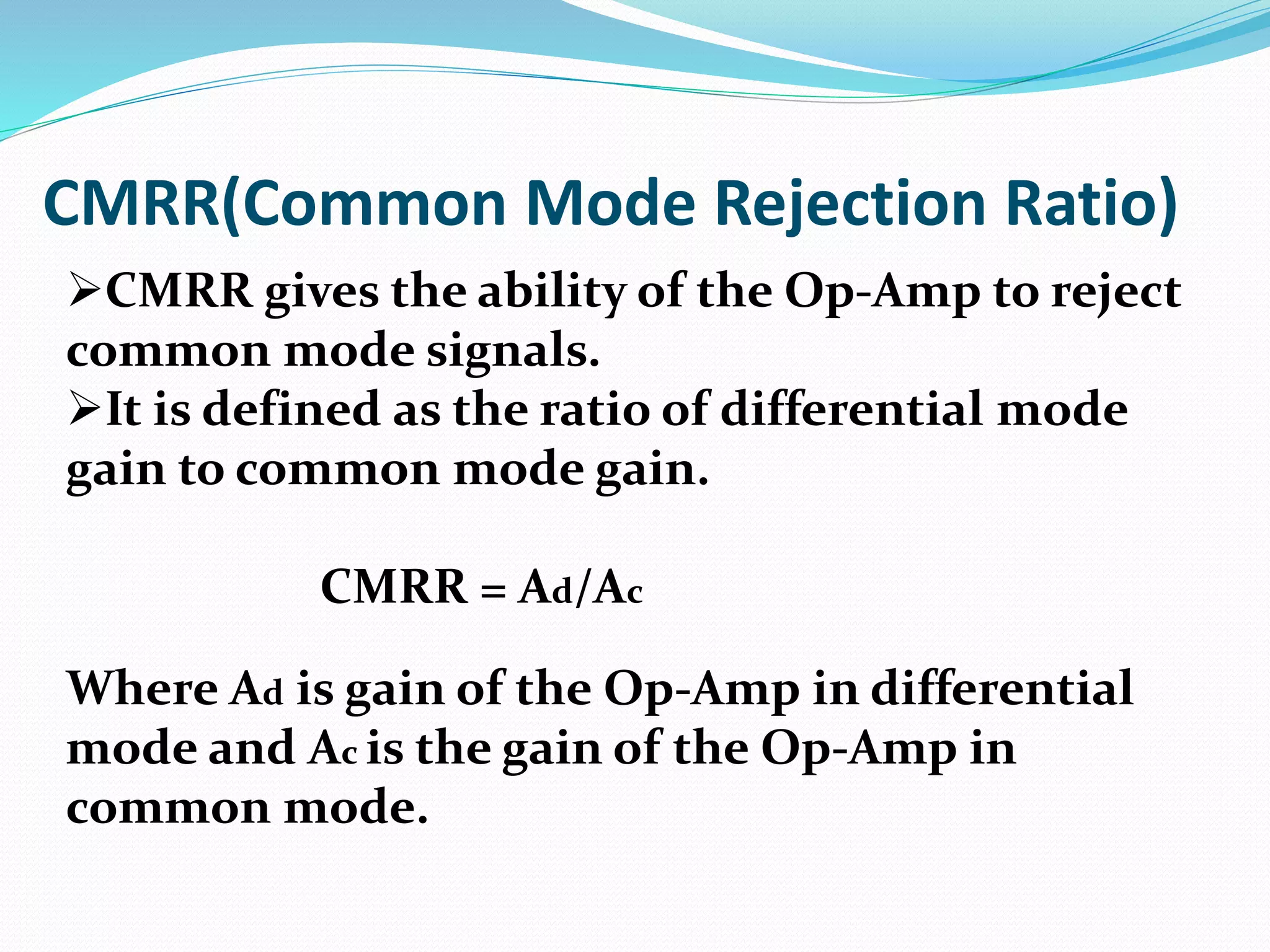
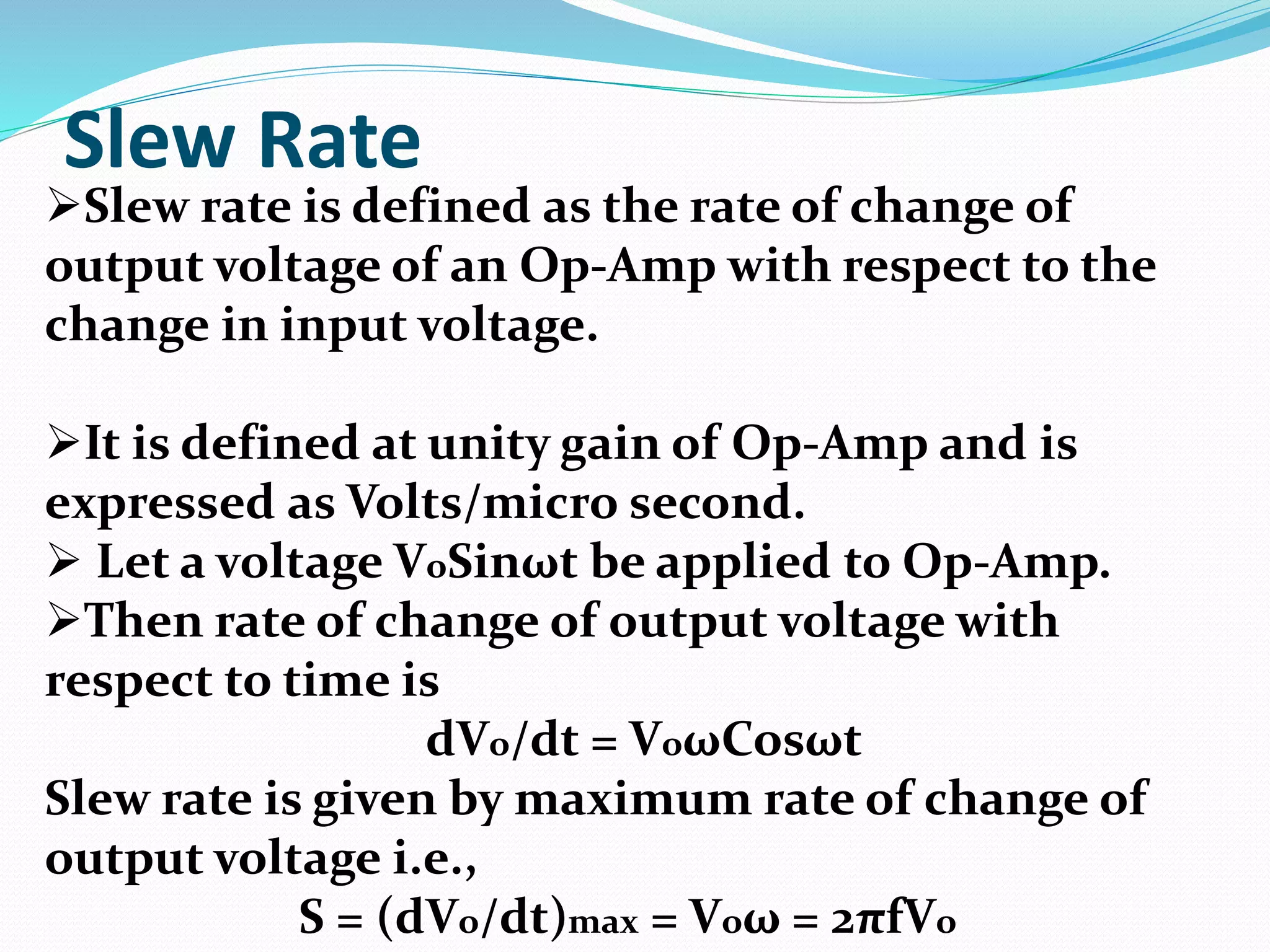
This document defines and describes several key parameters of operational amplifiers (op-amps): input offset voltage, output offset voltage, input offset current, input bias current, common mode rejection ratio (CMRR), and slew rate. It provides detailed explanations of each parameter, including their ideal and practical definitions, units of measurement, and symbols used. The document aims to comprehensively cover the technical specifications and characteristics of op-amps.