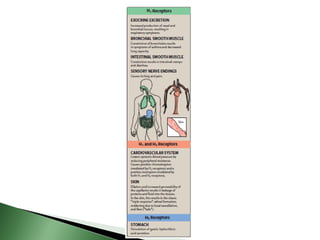
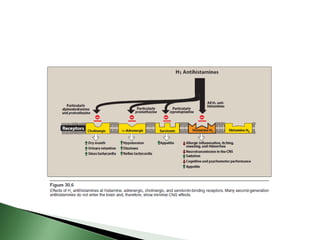
Histamine is a chemical messenger that mediates allergic and inflammatory reactions. It is synthesized and stored in mast cells and basophils before being released in response to stimuli. Histamine binds to H1, H2, H3, and H4 receptors, with the H1 and H2 receptors being clinically relevant drug targets. Antihistamines are used to treat allergic conditions by blocking H1 receptors, and H2 receptor blockers inhibit gastric acid secretion. First-generation antihistamines have greater sedative and anticholinergic side effects than second-generation drugs due to interactions with other receptors.