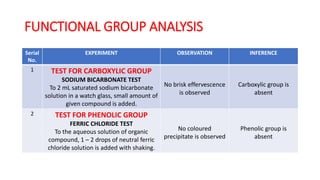
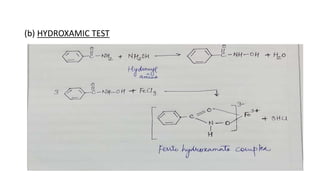
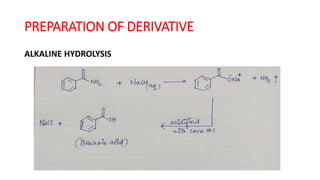
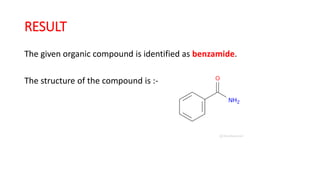
The document summarizes the systematic analysis of an unknown organic compound. Preliminary analysis involves physical tests and solubility tests to determine functional groups possibly present like acids, alcohols, amines. Further tests detect nitrogen and rule out sulfur and halogens. Reaction tests confirm the presence of an amide functional group. The melting point is determined to be 128°C. Through alkaline hydrolysis, the compound is identified as benzamide which yields benzoic acid, melting point 121°C upon reaction.