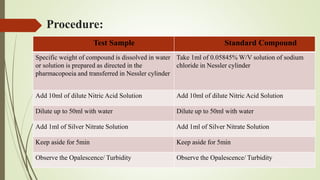
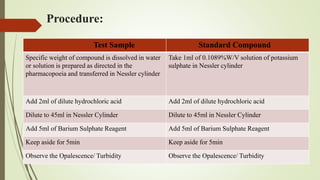
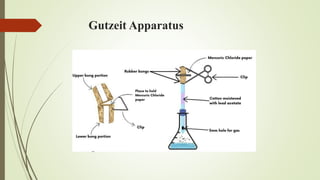
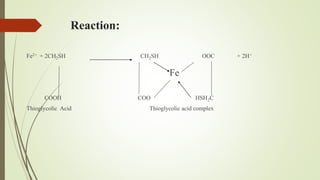
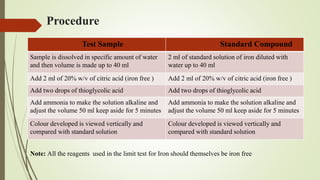
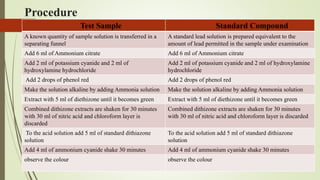
This document provides an introduction to pharmaceutical chemistry and discusses sources of errors and impurities in pharmaceuticals. It describes how impurities can affect pharmacopoeial substances by making them toxic, decreasing therapeutic effects, or changing physical/chemical properties. Common impurity tests are outlined, including limit tests for chlorides, sulfates, arsenic, and iron which use chemical reactions to identify impurities and compare results to standards. Proper procedures and reasons for each test are explained in detail.