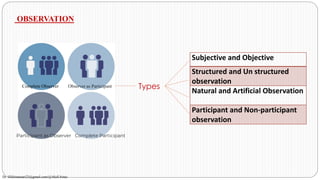
This document outlines objectives and content for a unit on developing alternative techniques for test development and evaluation. It discusses the process of classroom observation, including planning, formats for observation, and deriving results. It also covers classroom projects, defining projects, describing types of projects, and outlining the phases of a project, from creating a situation to reporting. Tasks are distinguished from tests, and characteristics and indicators of successful projects are provided. The document provides guidance on implementing projects in the classroom, including forming groups, developing timelines, and conducting assessments.